A Global Tapestry of Mountains: Understanding the World’s Majestic Ranges
Related Articles: A Global Tapestry of Mountains: Understanding the World’s Majestic Ranges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Global Tapestry of Mountains: Understanding the World’s Majestic Ranges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Tapestry of Mountains: Understanding the World’s Majestic Ranges
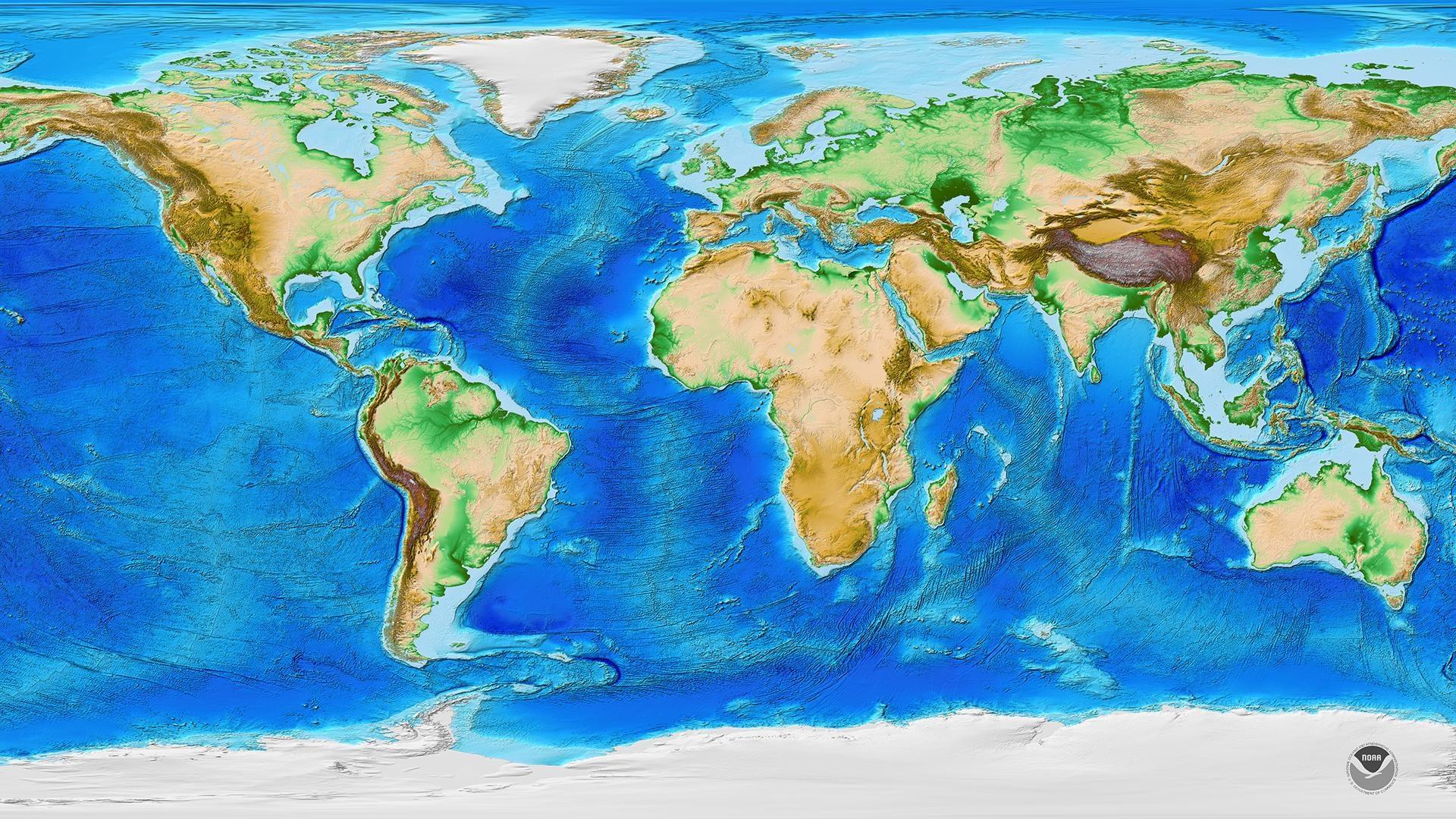
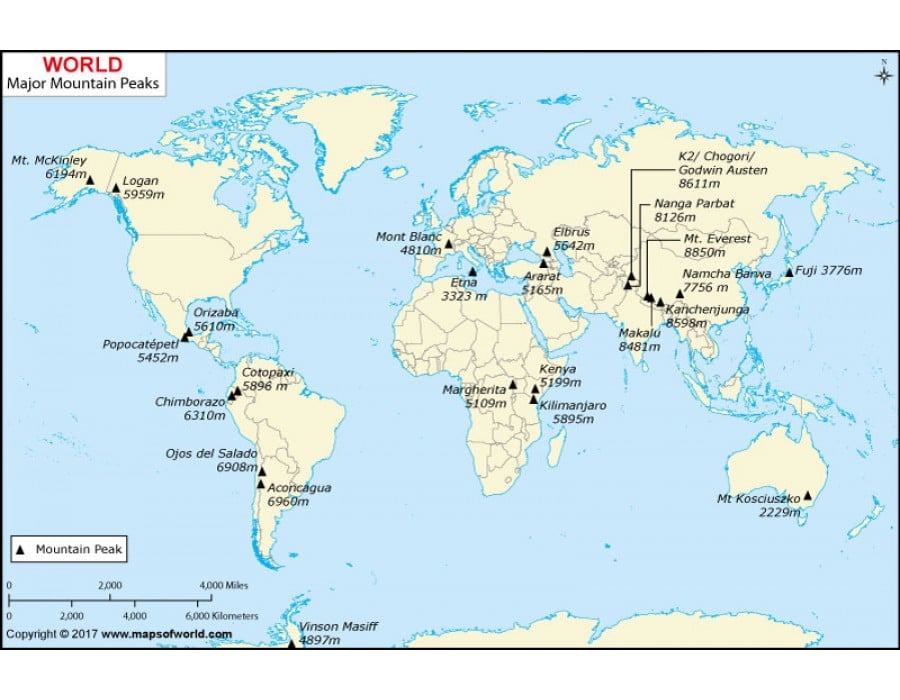
Mountains, those imposing landforms that pierce the sky, are not mere geographical features. They are intricate ecosystems, cradles of biodiversity, and vital contributors to global climate patterns. Their majestic presence shapes the landscapes, cultures, and histories of the world, offering a glimpse into the planet’s dynamic geological processes. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these mountain ranges provides a crucial lens through which to appreciate the complexity and interconnectedness of Earth’s systems.
The Tectonic Tapestry: The Birth of Mountains
The formation of mountain ranges is a testament to the restless nature of Earth’s crust. Driven by the relentless movement of tectonic plates, these massive landmasses collide, buckle, and fold, giving rise to the towering peaks and deep valleys that define our planet’s topography.
-
Convergent Plate Boundaries: The most prominent mountain ranges, including the Himalayas, Andes, and Alps, emerge at convergent plate boundaries. Here, two tectonic plates collide, forcing one plate to slide beneath the other (subduction) or to buckle upwards. This process generates intense pressure and heat, leading to the formation of fold mountains.
-
Continental Collisions: When two continental plates collide, their immense weight and resistance to subduction result in the formation of massive mountain ranges. The Himalayas, for instance, were formed by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates.
-
Volcanic Mountains: Volcanic mountains, like those found in the Andes and the Cascade Range, arise from the eruption of magma from Earth’s mantle. The accumulated lava and ash solidify, forming conical peaks.
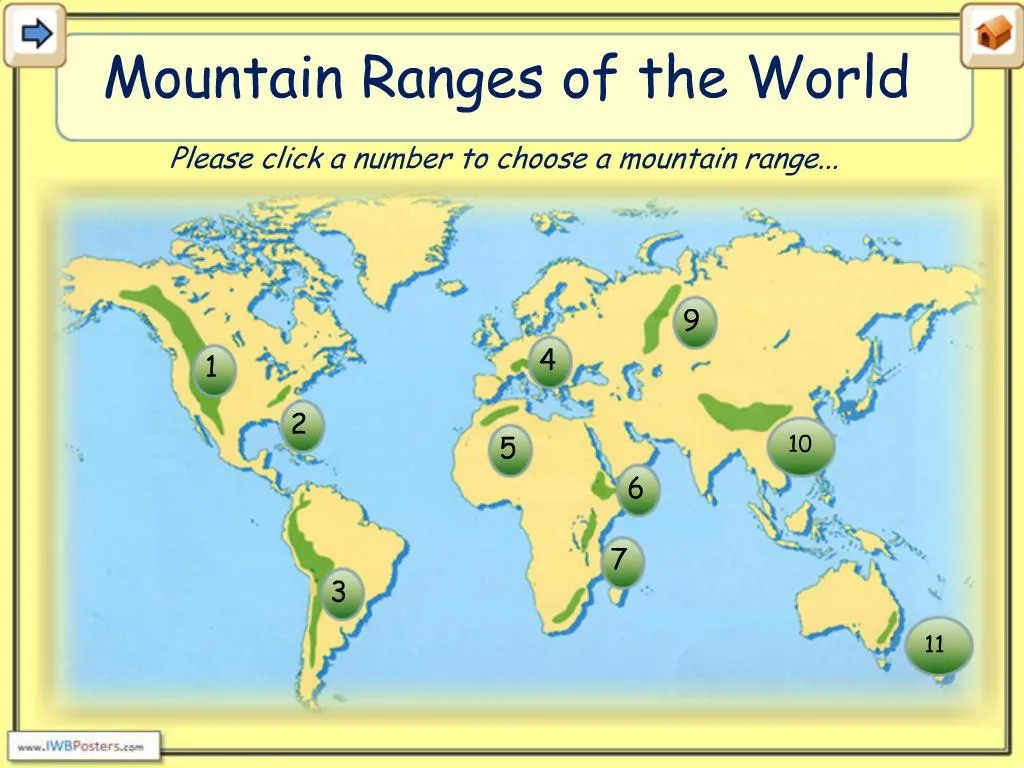
Global Mountain Ranges: A Continental Overview
The world’s mountain ranges are not randomly scattered across the globe; they form distinct belts that often coincide with tectonic plate boundaries. Examining these ranges provides a deeper understanding of their formation and the unique features they possess.
-
The Circum-Pacific Belt: This belt, often referred to as the "Ring of Fire," encircles the Pacific Ocean and is characterized by intense volcanic activity and frequent earthquakes. It is home to some of the world’s most impressive mountain ranges, including the Andes in South America, the Rocky Mountains in North America, and the Japanese Alps.
-
The Alpine-Himalayan Belt: This belt stretches from the Alps in Europe, through the Caucasus Mountains, and culminates in the Himalayas. It is a result of the collision between the Eurasian and African plates, giving rise to some of the highest peaks on Earth.
-
The North American Cordillera: This vast mountain range stretches from Alaska to Mexico and encompasses the Rocky Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, and the Coast Mountains. Its formation is attributed to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate.
-
The African Mountain Ranges: The African continent boasts a diverse range of mountains, including the Atlas Mountains in the north, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the Drakensberg Mountains in the south. These ranges are a result of various geological processes, including tectonic activity and volcanic eruptions.
The Importance of Mountain Ranges
Mountain ranges are not merely aesthetic features; they play a vital role in shaping the planet’s environment and supporting life.
-
Climate Regulation: Mountains act as barriers to wind and moisture, influencing precipitation patterns and creating distinct microclimates on either side. They also contribute to the formation of clouds and precipitation, playing a critical role in the global water cycle.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountain ranges are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity. Their diverse elevations, slopes, and microclimates provide a mosaic of habitats that support a wide array of plant and animal species. Many endemic species, found only in specific mountain regions, thrive in these unique ecosystems.
-
Water Resources: Mountains are often referred to as "water towers" due to their role in collecting and storing water. Snowmelt from mountain glaciers and rainfall provide vital water sources for rivers, lakes, and aquifers, supporting human populations and ecosystems downstream.
-
Natural Resources: Mountain ranges harbor valuable mineral deposits, timber resources, and hydropower potential. These resources have historically played a significant role in economic development and continue to be essential for modern societies.
Challenges and Opportunities
While mountain ranges offer numerous benefits, they also face challenges related to climate change, human activities, and conservation efforts.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Melting glaciers, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risks of natural disasters pose significant challenges to mountain ecosystems and the communities that depend on them.
-
Human Impacts: Deforestation, mining, and unsustainable agriculture practices threaten mountain biodiversity and the integrity of their ecosystems.
-
Conservation Efforts: Protecting mountain ranges requires collaborative efforts from governments, communities, and international organizations. Sustainable land management practices, conservation initiatives, and promoting responsible tourism are crucial for ensuring the long-term health of these vital ecosystems.
FAQs
Q: What is the highest mountain range in the world?
A: The Himalayas, located in Asia, is the highest mountain range in the world, with Mount Everest, at 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet), being the highest peak on Earth.
Q: What is the difference between a mountain and a hill?
A: While there is no universally agreed-upon distinction, mountains are generally considered to be higher and more prominent than hills. Typically, mountains are considered to rise at least 1,000 feet above their surroundings, while hills are lower.
Q: What is a mountain range?
A: A mountain range is a series of mountains that are geologically connected and share a similar origin. They are often formed by the same tectonic forces and typically have a common alignment or orientation.
Q: How do mountains affect the climate?
A: Mountains act as barriers to wind and moisture, creating distinct microclimates on either side. They also influence precipitation patterns and contribute to the formation of clouds. The elevation and orientation of mountain ranges can significantly impact regional weather patterns.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing mountain ecosystems?
A: Challenges include climate change impacts, such as melting glaciers and altered precipitation patterns; human impacts, such as deforestation, mining, and unsustainable agriculture; and the need for effective conservation efforts to protect biodiversity and ensure sustainable resource management.
Tips
-
Embrace the Power of Maps: Utilize world maps and topographic maps to visualize the distribution of mountain ranges, their relationships to tectonic plates, and their impact on global geography.
-
Explore Mountain Cultures: Learn about the diverse cultures and communities that have thrived in mountainous regions. Understand their unique adaptations, traditions, and contributions to human history.
-
Support Sustainable Mountain Tourism: Choose responsible tourism operators who prioritize environmental protection, cultural sensitivity, and local community involvement.
-
Advocate for Mountain Conservation: Support organizations and initiatives working to protect mountain ecosystems, promote sustainable land management practices, and address climate change impacts.
Conclusion
Mountain ranges are not merely geographical features; they are intricate ecosystems, vital contributors to global climate patterns, and cultural landscapes that have shaped human history. Their majestic presence reminds us of the dynamic forces that shape our planet and the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems. Understanding and appreciating these magnificent landforms is crucial for promoting sustainable development, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring the well-being of both human and natural communities. By embracing the power of maps, exploring mountain cultures, and supporting conservation efforts, we can contribute to the preservation of these invaluable natural treasures for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Tapestry of Mountains: Understanding the World’s Majestic Ranges. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!