A Global Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the World’s Mountains
Related Articles: A Global Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the World’s Mountains
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Global Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the World’s Mountains. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Global Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the World’s Mountains
The Earth’s surface is a diverse and dynamic landscape, sculpted by geological forces over millions of years. Among these formations, mountains stand as majestic testaments to the planet’s power and history. These towering structures are not merely geographical features; they are ecosystems, cultural landscapes, and vital resources, shaping life and influencing human civilization in profound ways.
The Genesis of Mountain Ranges:
Mountains are born from the tectonic plates that compose the Earth’s crust. These plates are constantly in motion, driven by the heat within the planet’s core. When plates collide, the immense pressure causes the land to buckle, fold, and uplift, creating mountain ranges. This process, known as orogeny, can take millions of years to complete.
There are two primary types of mountain formation:
- Convergent Plate Boundaries: When two continental plates collide, their equal density leads to a process known as "continental collision." This results in the formation of large, towering mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, the Alps, and the Andes.
- Ocean-Continent Convergence: When an oceanic plate, denser than a continental plate, collides, the oceanic plate subducts beneath the continental plate. This process creates volcanic arcs and mountain ranges, like the Cascade Range in North America and the Andes Mountains.
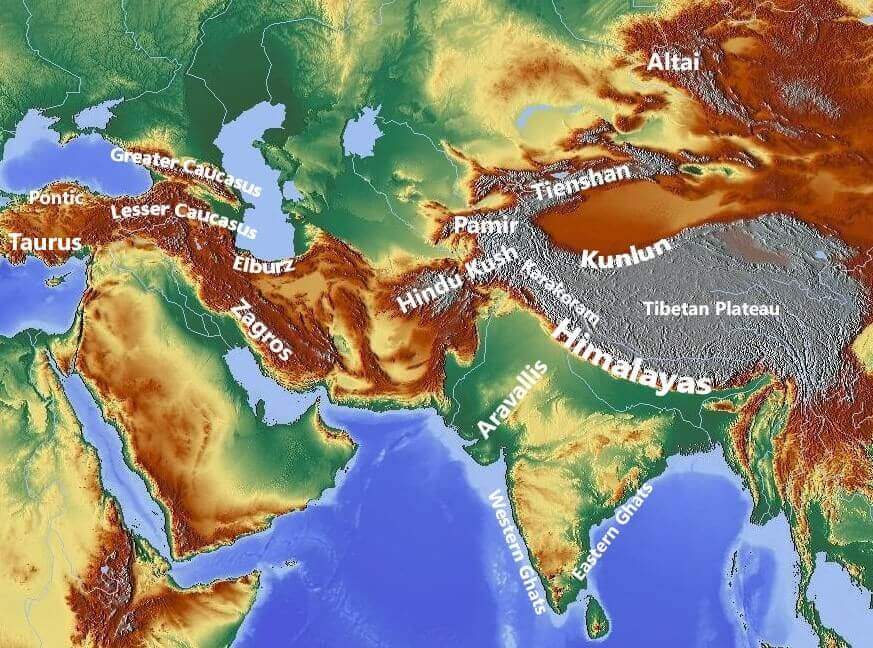
World Map Mountains: A Global Perspective:
The world map is an invaluable tool for understanding the distribution and significance of mountains across the globe. It reveals a tapestry of peaks, each with its unique story and characteristics:
- The Himalayas: The highest mountain range in the world, the Himalayas, are a product of the collision between the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates. Home to Mount Everest, the highest peak above sea level, the Himalayas are a symbol of human ambition and the power of nature.
- The Andes Mountains: Stretching along the western edge of South America, the Andes are the longest mountain range on Earth. They are a diverse landscape, ranging from snow-capped peaks to lush rainforests, and are home to a rich variety of flora and fauna.
- The Alps: Located in Europe, the Alps are a majestic range that has inspired artists, writers, and adventurers for centuries. They are a popular destination for skiing, hiking, and mountaineering, and are also a crucial source of water for surrounding regions.
- The Rocky Mountains: Spanning the western United States and Canada, the Rockies are a vast and rugged range known for its stunning scenery and abundant wildlife. They are a vital source of natural resources, including timber, minerals, and water.
- The Atlas Mountains: Situated in North Africa, the Atlas Mountains are a unique range that separates the Mediterranean coast from the Sahara Desert. They are home to a diverse array of cultures and traditions, and are a vital source of water for the region.
The Importance of World Map Mountains:
Mountains are not simply geographical features; they play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s climate, biodiversity, and human civilization.
- Climate Regulation: Mountains act as natural barriers, influencing wind patterns and precipitation. They can create rain shadows on their leeward sides, leading to drier conditions, while their windward sides often receive significant rainfall.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountains are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. Their varied altitudes and microclimates provide unique habitats for diverse life forms.
- Water Resources: Mountains are often the source of rivers and streams, providing essential water for agriculture, industry, and human consumption. They also play a crucial role in regulating water cycles and preventing soil erosion.
- Cultural Heritage: Mountains have long held spiritual and cultural significance for human societies. They are often seen as sacred places, and their landscapes have inspired art, literature, and music.
- Tourism and Recreation: Mountains offer breathtaking scenery and challenging outdoor experiences, attracting tourists and adventurers from around the world. They provide opportunities for hiking, climbing, skiing, and other recreational activities.
FAQs About World Map Mountains:
- What is the highest mountain in the world? Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas, is the highest peak above sea level, reaching a height of 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet).
- What is the difference between a mountain and a hill? Generally, a mountain is defined as a landform with an elevation of at least 1,000 feet (304.8 meters) above sea level, while a hill is typically lower.
- How do mountains affect climate? Mountains influence wind patterns, precipitation, and temperature, creating diverse microclimates and affecting regional weather patterns.
- What are some of the environmental challenges facing mountains? Mountain ecosystems face threats from climate change, deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable tourism.
- How can we protect mountains? Conservation efforts include establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable tourism, and addressing climate change.
Tips for Studying World Map Mountains:
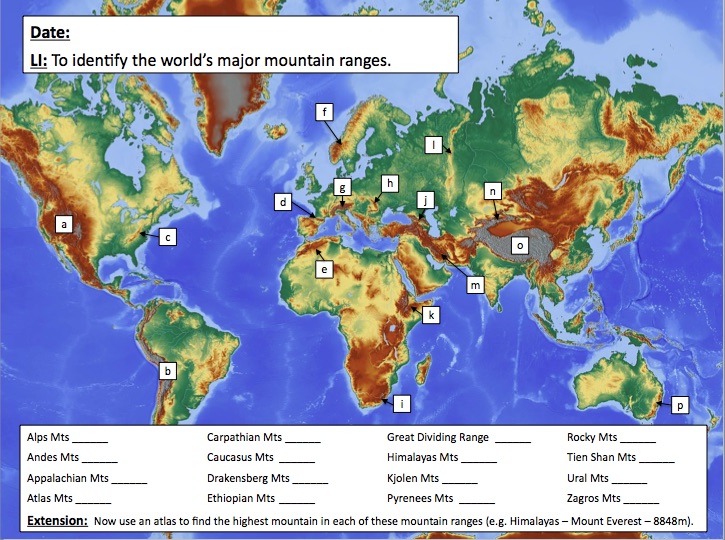
- Use a physical world map: A physical world map clearly displays the topography of the Earth, allowing you to visualize mountain ranges and their relative heights.
- Explore online resources: Websites and databases provide detailed information about individual mountain ranges, including their geological history, biodiversity, and cultural significance.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous books and articles available that offer in-depth insights into the geology, ecology, and human history of mountains.
- Travel to mountains: If possible, visit mountain ranges to experience their beauty and grandeur firsthand. Observe the diverse landscapes, meet local communities, and learn about their unique cultures.
Conclusion:
The world map mountains are a testament to the Earth’s geological history and the diversity of life on our planet. They are vital ecosystems, cultural landscapes, and sources of essential resources. Understanding the significance of mountains is crucial for appreciating their role in shaping our world and for ensuring their protection for future generations. By studying world map mountains, we gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s dynamic processes and the interconnectedness of all living things.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Global Tapestry of Peaks: Exploring the World’s Mountains. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!