Charting the Landscape: The Crucial Role of Map Makers in the Middle East
Related Articles: Charting the Landscape: The Crucial Role of Map Makers in the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Landscape: The Crucial Role of Map Makers in the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Landscape: The Crucial Role of Map Makers in the Middle East

The Middle East, a region of immense cultural, economic, and geopolitical significance, is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, intricate histories, and complex societal dynamics. Understanding this intricate tapestry requires a robust foundation of spatial knowledge, a role that map makers play with critical importance.
The Foundation of Spatial Understanding:
Maps are more than just static representations of geographical features; they are powerful tools that illuminate the complexities of the human experience. In the Middle East, where history, politics, and geography are inextricably intertwined, maps serve as vital instruments for:
-
Navigating a Diverse Landscape: The Middle East encompasses a wide range of terrains, from the snow-capped peaks of the Taurus Mountains to the arid deserts of the Arabian Peninsula. Maps provide essential guidance for navigation, transportation, and resource management, facilitating movement across these diverse landscapes.
-
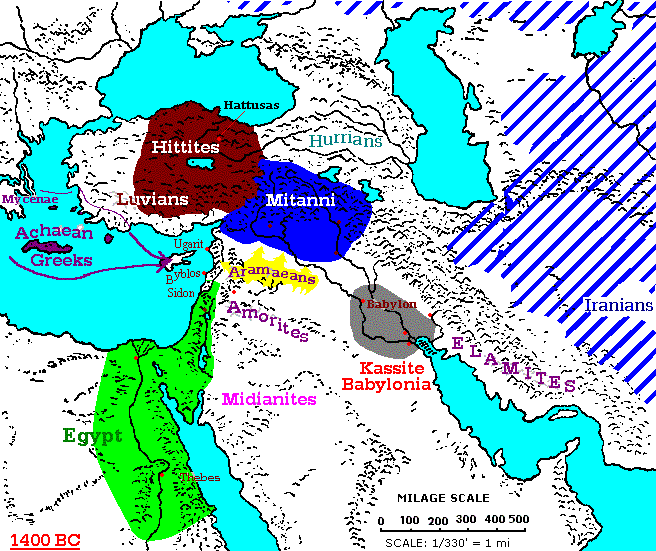
Understanding Historical and Cultural Connections: Maps are crucial for tracing the flow of history, migration patterns, and the spread of cultural influences. They illuminate the interconnectedness of civilizations and shed light on the intricate tapestry of human interaction throughout the region.
-
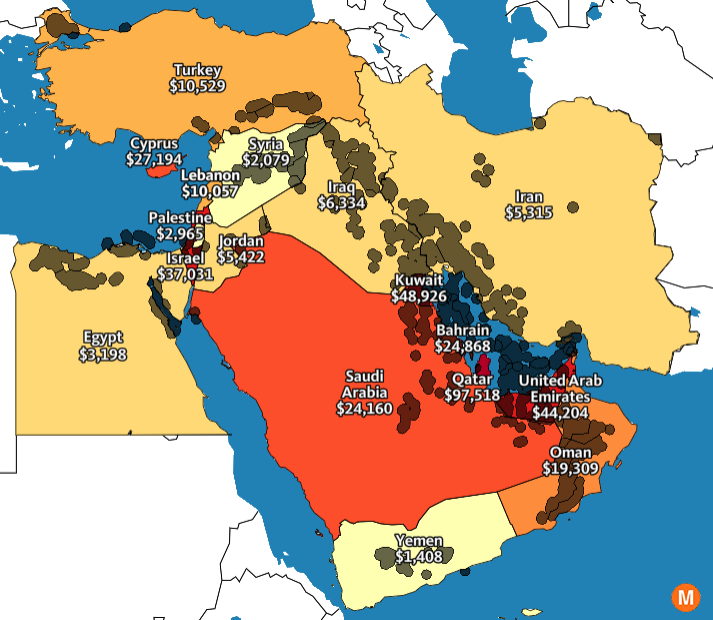
Visualizing Political and Economic Dynamics: Maps are essential for understanding the geopolitical landscape of the Middle East. They depict borders, resource distribution, trade routes, and population densities, providing valuable insights into the region’s complex political and economic realities.
-
Supporting Development and Planning: Maps are indispensable for planning infrastructure projects, managing natural resources, and fostering sustainable development. They enable efficient resource allocation, infrastructure development, and environmental protection, contributing to the region’s economic growth and social well-being.
The Evolution of Map Making in the Middle East:
The practice of map making in the Middle East has a rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations. Early maps, often inscribed on clay tablets or papyrus, served as navigational tools, depicting trade routes, settlements, and key geographical features.
The Islamic Golden Age witnessed a significant advancement in cartography. Arab scholars and cartographers developed sophisticated techniques for map creation, incorporating astronomical observations, mathematical calculations, and precise measurements. Notable contributions include the development of the astrolabe, a navigational instrument that revolutionized mapmaking, and the creation of detailed world maps that incorporated knowledge from various cultures.
In the modern era, map making in the Middle East has undergone a significant transformation. The advent of satellite imagery, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and digital mapping technologies has revolutionized the field, enabling the creation of highly detailed and interactive maps.
The Impact of Modern Technologies:
Modern mapping technologies have significantly enhanced the capabilities of map makers in the Middle East, enabling them to:
-
Create High-Resolution Maps: Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide unprecedented detail, allowing for the creation of highly accurate maps that capture intricate features of the landscape.
-
Develop Interactive Maps: GIS software empowers map makers to create dynamic and interactive maps that allow users to explore data layers, analyze patterns, and gain deeper insights into the region’s complexities.
-
Facilitate Data Analysis: Modern mapping technologies allow for the integration and analysis of vast datasets, enabling map makers to visualize trends, predict patterns, and support informed decision-making across various sectors.
-
Promote Transparency and Collaboration: Online mapping platforms and open-source data initiatives foster transparency and collaboration, enabling researchers, policymakers, and citizens to access and utilize spatial information for diverse purposes.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite the advancements in technology, map makers in the Middle East face several challenges:
-
Data Accessibility and Accuracy: Ensuring the availability of accurate and reliable data is crucial for creating comprehensive and trustworthy maps. Data gaps, inconsistencies, and limitations in data collection can hinder the effectiveness of mapping efforts.
-
Political and Security Concerns: In a region marked by political instability and conflict, access to data and the freedom to map certain areas can be restricted, posing challenges to map makers seeking to provide complete and unbiased representations of the landscape.
-
Technological Infrastructure and Capacity Building: The widespread adoption of modern mapping technologies requires adequate infrastructure, training, and investment in capacity building. Bridging the digital divide and fostering a skilled workforce are crucial for maximizing the potential of these technologies.
The Importance of Map Makers in the Middle East:
Map makers play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the Middle East, fostering informed decision-making, and supporting sustainable development. Their work contributes to:
-
Resource Management: Maps are essential for identifying and managing natural resources, including water, land, and minerals. They enable efficient resource allocation, environmental protection, and sustainable economic development.
-
Infrastructure Development: Maps are crucial for planning and implementing infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and energy networks. They facilitate efficient design, construction, and maintenance, contributing to the region’s connectivity and economic growth.
-
Disaster Response and Mitigation: Maps are vital for preparing for and responding to natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, and droughts. They provide real-time information on affected areas, facilitate rescue operations, and support disaster mitigation efforts.
-
Conflict Resolution and Peacebuilding: Maps can play a role in conflict resolution and peacebuilding by providing objective representations of disputed territories, facilitating negotiations, and supporting peace agreements.
-
Cultural Heritage Preservation: Maps are essential for documenting and preserving cultural heritage sites, including archaeological sites, historical landmarks, and traditional settlements. They help in understanding the region’s rich cultural tapestry and promoting responsible tourism.
FAQs by Map Maker Middle East:
Q: What are the most important aspects of map making in the Middle East?
A: The most important aspects of map making in the Middle East include:
- Understanding the region’s diverse landscape: This includes accurately depicting geographical features, elevation changes, and natural resources.
- Reflecting the region’s historical and cultural context: Maps should incorporate historical information, migration patterns, and cultural influences to provide a holistic understanding of the region.
- Visualizing the geopolitical landscape: This includes depicting borders, resource distribution, population densities, and conflict zones to provide insights into the region’s complexities.
- Supporting development and planning: Maps are crucial for planning infrastructure projects, managing natural resources, and fostering sustainable development.
Q: What are the challenges faced by map makers in the Middle East?
A: Map makers in the Middle East face challenges such as:
- Data accessibility and accuracy: Ensuring access to accurate and reliable data is crucial for creating comprehensive and trustworthy maps.
- Political and security concerns: Access to data and the freedom to map certain areas can be restricted due to political instability and conflict.
- Technological infrastructure and capacity building: The widespread adoption of modern mapping technologies requires adequate infrastructure, training, and investment in capacity building.
Q: How can map makers contribute to peacebuilding and conflict resolution in the Middle East?
A: Map makers can contribute to peacebuilding and conflict resolution by:
- Providing objective representations of disputed territories: This can facilitate negotiations and help build trust between parties.
- Mapping conflict-related data: This can provide insights into the causes and consequences of conflict, informing peacebuilding efforts.
- Supporting the implementation of peace agreements: Maps can be used to monitor the implementation of agreements and ensure compliance.
Tips by Map Maker Middle East:
- Collaborate with local communities: Engaging with local communities can provide valuable insights into the region’s complexities and ensure that maps reflect local perspectives.
- Promote open-source data initiatives: This can foster transparency and collaboration, enabling researchers, policymakers, and citizens to access and utilize spatial information.
- Invest in capacity building: Training and equipping local map makers with the skills and resources they need is crucial for fostering a skilled workforce and maximizing the potential of modern mapping technologies.
- Advocate for responsible data collection and use: Ensuring that data is collected ethically and used responsibly is essential for building trust and promoting sustainable development.
Conclusion:
Map makers play a vital role in navigating the complex landscape of the Middle East, providing a foundation for understanding its diverse geography, history, culture, and politics. As technology continues to evolve, map makers have the opportunity to leverage modern tools and methodologies to create increasingly comprehensive and insightful representations of the region. By addressing the challenges they face and embracing the opportunities presented by new technologies, map makers can contribute to sustainable development, peacebuilding, and a deeper understanding of the Middle East’s rich and dynamic tapestry.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Landscape: The Crucial Role of Map Makers in the Middle East. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!