Charting the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Map Makers
Related Articles: Charting the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Map Makers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Map Makers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Map Makers

Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, hold a wealth of information about the Earth’s surface. They are essential tools for a wide range of applications, from urban planning and resource management to military operations and outdoor recreation. The creation of these maps, however, is a complex process requiring specialized software known as topographic map makers. This article delves into the intricacies of these tools, exploring their functionalities, importance, and the benefits they offer.
Understanding the Essence of Topographic Map Makers
Topographic map makers are sophisticated software programs designed to generate detailed representations of the Earth’s surface. They utilize a variety of data sources, including aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and ground surveys, to construct accurate depictions of elevation, terrain features, and geographical elements. These programs employ advanced algorithms and mathematical models to transform raw data into visually compelling and informative maps.
Key Components and Functionalities
Topographic map makers encompass a range of functionalities that enable them to generate comprehensive and accurate maps:
- Data Acquisition and Processing: These programs facilitate the integration and processing of data from diverse sources, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scans, aerial photographs, and GPS measurements. They employ sophisticated algorithms to convert raw data into usable formats, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Terrain Modeling: Topographic map makers utilize specialized algorithms to create digital terrain models (DTMs) and digital elevation models (DEMs). These models represent the Earth’s surface in three dimensions, providing precise elevation data and enabling the generation of contour lines, hillshades, and other visual representations.
- Feature Extraction: These programs allow users to identify and extract various geographical features from the processed data, such as roads, buildings, rivers, and forests. They offer tools for symbolizing and labeling these features, enhancing the map’s readability and providing valuable information.
- Map Projection and Layout: Topographic map makers provide options for selecting appropriate map projections and layouts. This ensures accurate representation of geographical features and distances, considering the Earth’s curvature and the intended map scale.
- Customization and Output: These programs offer extensive customization options for map styles, symbols, and legends. Users can tailor the maps to specific needs and applications, ensuring clarity and ease of interpretation. They also allow for exporting maps in various formats, including digital images, vector graphics, and printable files.
Benefits of Utilizing Topographic Map Makers
The use of topographic map makers offers numerous benefits across various sectors:
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing comprehensive and accurate spatial data, these tools enable informed decision-making in diverse fields, including urban planning, resource management, infrastructure development, and environmental monitoring.
- Enhanced Safety and Efficiency: Topographic maps generated by these programs facilitate safe navigation, particularly in challenging terrains. They provide crucial information for disaster response, search and rescue operations, and construction projects, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Effective Communication and Visualization: Topographic maps offer a powerful tool for communicating complex spatial information to diverse audiences. They provide a clear and intuitive visual representation of the terrain, facilitating understanding and collaboration.
- Streamlined Workflow: Topographic map makers streamline the map-making process, automating repetitive tasks and reducing errors. They provide a comprehensive platform for managing and analyzing geospatial data, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By automating tasks and eliminating the need for manual map creation, topographic map makers contribute to cost savings. They also enable the efficient use of data, minimizing the need for redundant surveys and data collection.
FAQs about Topographic Map Makers
Q: What are the different types of data sources used by topographic map makers?
A: Topographic map makers utilize a variety of data sources, including:
- Aerial Photographs: These provide high-resolution images of the Earth’s surface, capturing details of terrain features, vegetation, and infrastructure.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite-based sensors capture data from various wavelengths, providing information about elevation, vegetation cover, and land use.
- LiDAR Scans: LiDAR technology emits laser pulses that measure distances to the ground, creating highly accurate elevation models.
- Ground Surveys: Traditional surveying methods, involving measurements of distances, angles, and elevations, provide detailed information about specific locations.
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing a topographic map maker?
A: When selecting a topographic map maker, it is crucial to consider:
- Functionality: Ensure the software offers the necessary functionalities to meet specific requirements, such as data processing, terrain modeling, feature extraction, and map customization.
- Data Compatibility: Verify that the software supports the desired data formats and sources, ensuring seamless integration and processing.
- Ease of Use: Select a user-friendly interface that facilitates efficient data analysis, map creation, and customization.
- Cost and Licensing: Evaluate the software’s pricing structure and licensing terms to ensure compatibility with budget constraints.
- Technical Support: Choose a software provider that offers reliable technical support and documentation, ensuring smooth operation and problem resolution.
Tips for Effective Use of Topographic Map Makers
- Understand Data Sources: Familiarize yourself with the characteristics and limitations of different data sources to make informed decisions about their suitability for specific applications.
- Plan and Define Objectives: Clearly define the project’s objectives and scope before starting the map-making process. This will ensure that the generated maps meet the required specifications.
- Utilize Available Tools: Leverage the software’s functionalities to simplify tasks, automate processes, and enhance map accuracy.
- Validate Results: Regularly validate the generated maps against reliable data sources to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Collaborate and Share: Encourage collaboration among team members and stakeholders to enhance map accuracy and ensure that they meet the needs of all involved parties.
Conclusion
Topographic map makers play a vital role in modern society, facilitating informed decision-making, enhancing safety and efficiency, and promoting effective communication across diverse sectors. These powerful tools enable the creation of accurate and comprehensive representations of the Earth’s surface, providing valuable insights into terrain features, elevation, and geographical elements. By leveraging their functionalities and adhering to best practices, users can harness the power of topographic map makers to drive innovation, promote sustainable development, and navigate the complexities of our world.
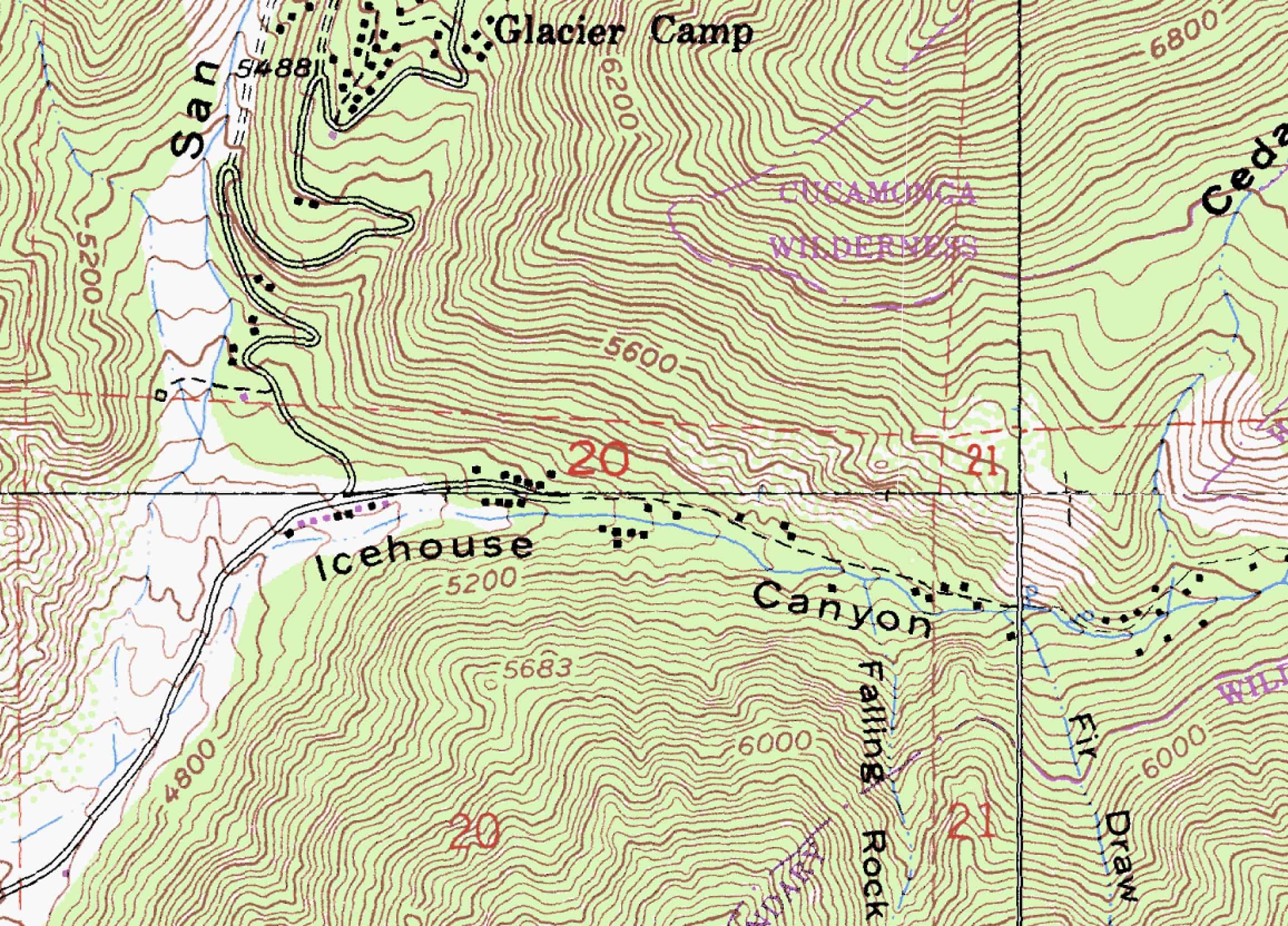
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/topomap2-56a364da5f9b58b7d0d1b406.jpg)

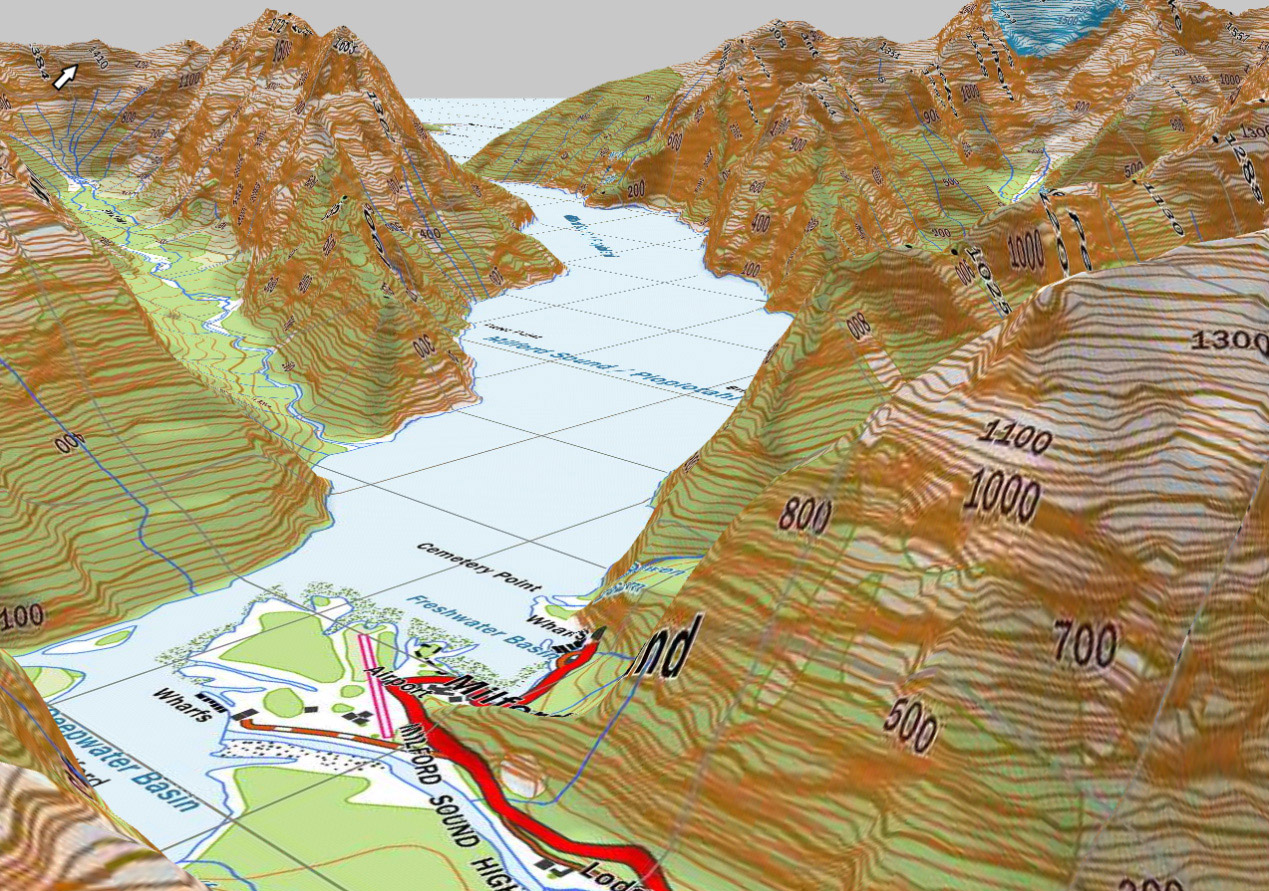

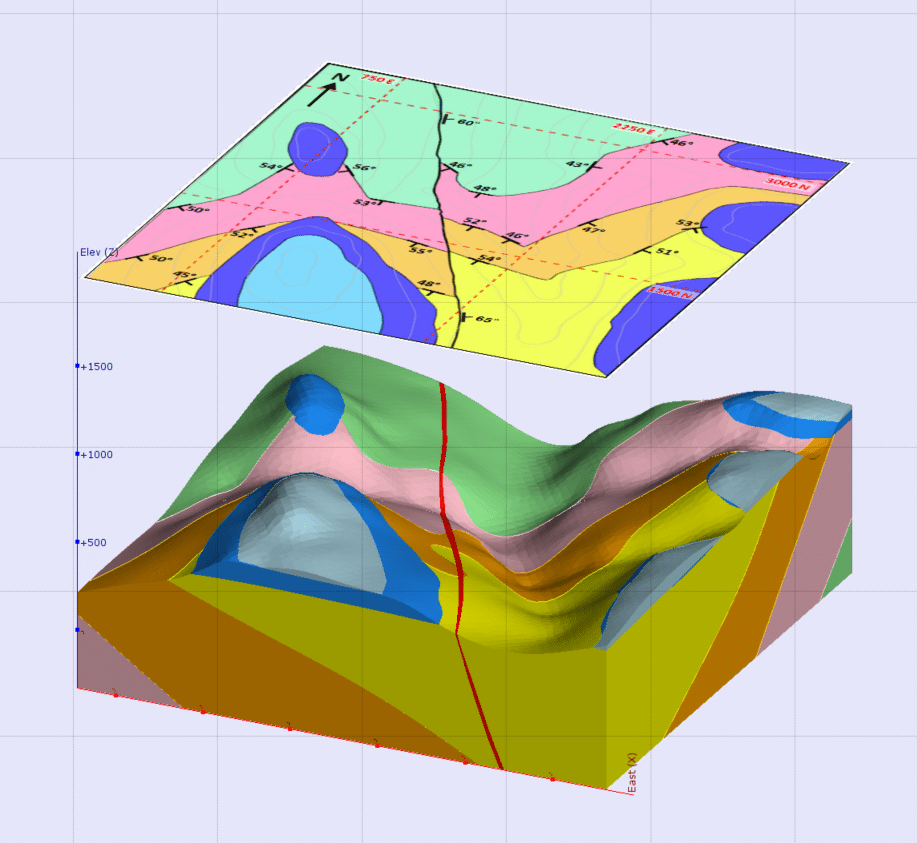

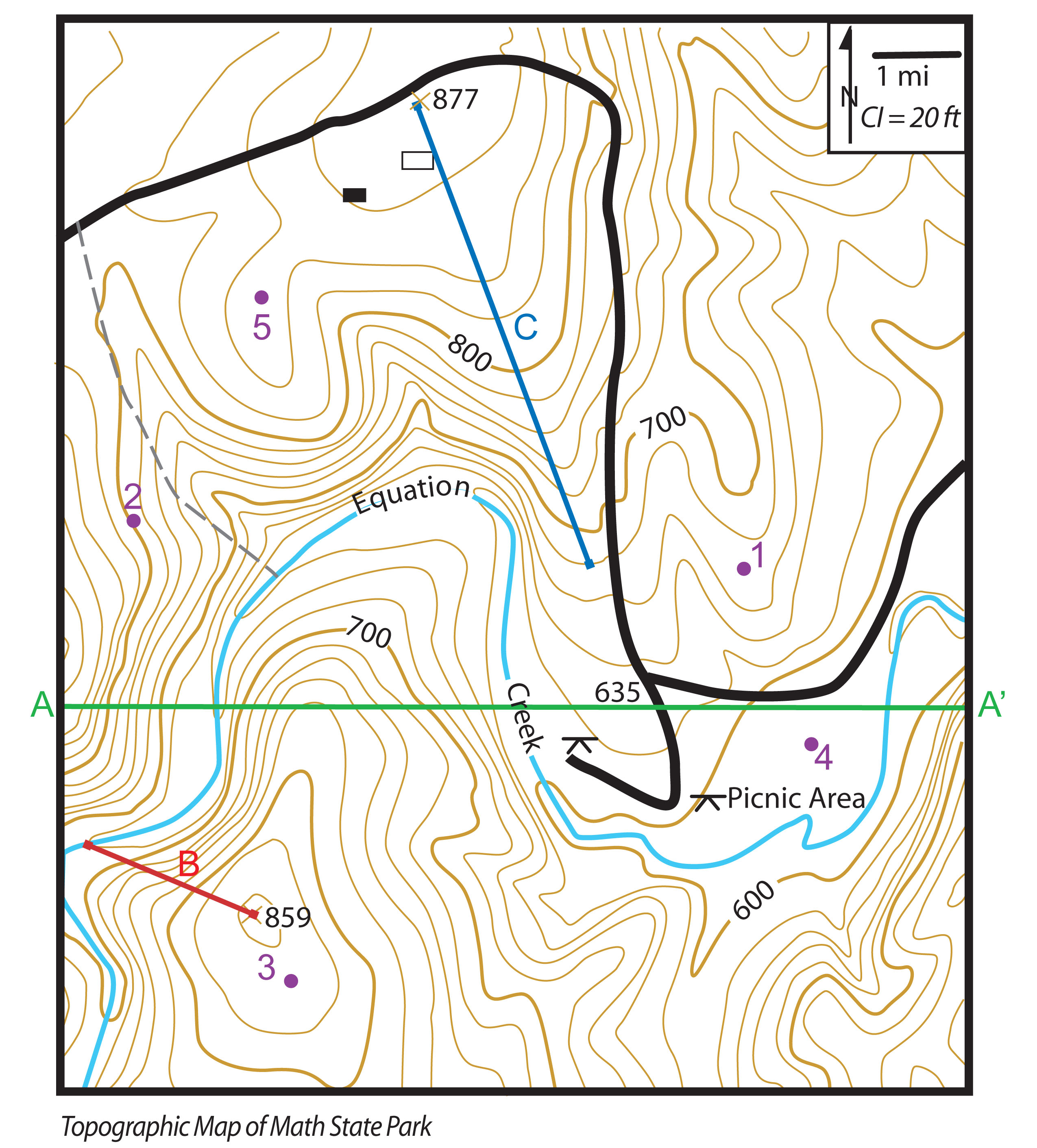
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Terrain: A Comprehensive Exploration of Topographic Map Makers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!