Navigating the Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude

Maps are essential tools for understanding our world, providing a visual representation of the Earth’s surface and its features. Within this intricate network of lines, two primary sets stand out: those that run north to south and those that run east to west. While the former, known as lines of longitude, are often associated with time zones and measuring distances east or west of a prime meridian, the latter, known as lines of latitude, play a crucial role in determining location, climate, and even the length of daylight hours.
The Foundation of Latitude:
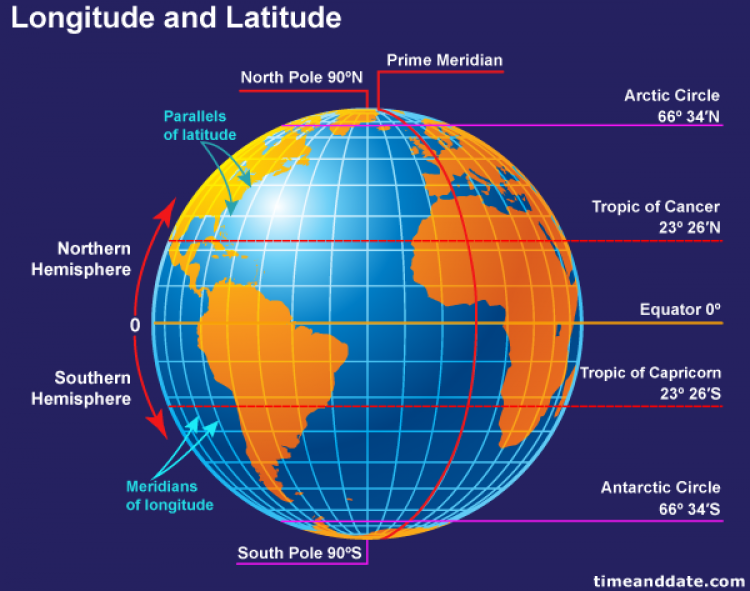
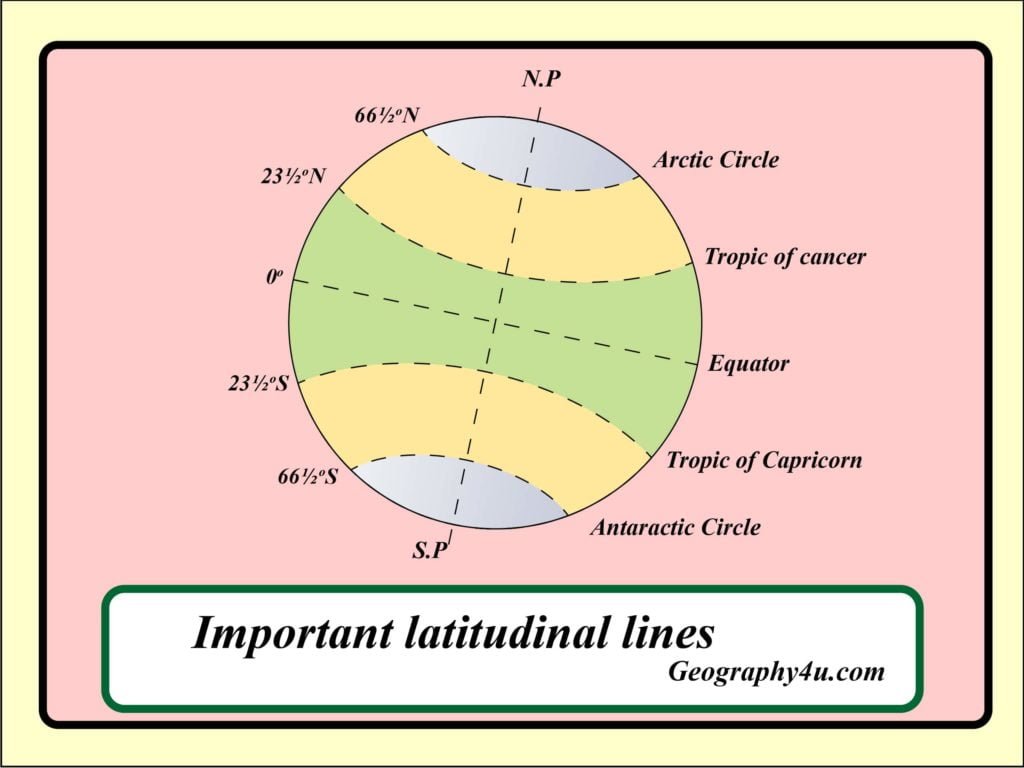
Imagine a giant, invisible circle encircling the Earth, passing through both the North and South Poles. This circle, known as the equator, forms the zero-degree line of latitude and divides the Earth into two hemispheres: the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Lines of latitude, also called parallels, are a series of circles parallel to the equator, extending from the North Pole to the South Pole. Each line represents a specific angular distance from the equator, measured in degrees.
Defining Location and Climate:
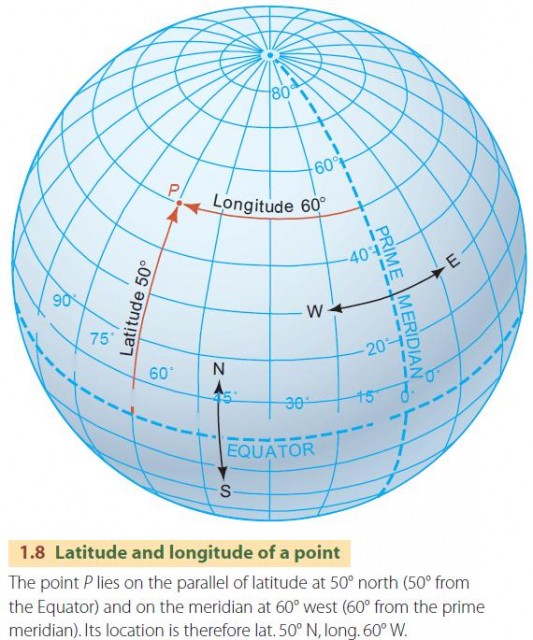
Lines of latitude provide a fundamental framework for pinpointing locations on Earth. They serve as coordinates, enabling us to identify a specific point on the globe by its latitude and longitude. For instance, the coordinates 40° N, 74° W pinpoint New York City’s location.
Beyond their role in locating places, lines of latitude influence climate patterns. The Earth’s tilt on its axis causes the sun’s rays to strike different parts of the planet at varying angles throughout the year. Regions located closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, leading to warmer temperatures and tropical climates. As one moves further away from the equator, towards higher latitudes, the angle of the sun’s rays decreases, resulting in colder climates.
Impact on Daylight Hours:
Lines of latitude also play a significant role in determining the length of daylight hours at different locations. The Earth’s rotation and its tilt create variations in the amount of sunlight received by different regions. During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere experiences its longest daylight hours, while the Southern Hemisphere experiences its shortest. Conversely, during the winter solstice, the Southern Hemisphere enjoys longer days, while the Northern Hemisphere experiences shorter days. The length of daylight hours increases as one moves closer to the equator and decreases as one moves towards the poles.
Navigational Tools and Mapping:
Lines of latitude have historically been crucial for navigation. Sailors relied on celestial observations to determine their latitude, using the position of stars and the sun relative to the horizon. This knowledge enabled them to chart their course and navigate across vast oceans.
In modern times, GPS systems and other technologies have replaced traditional methods of navigation. However, lines of latitude remain essential for mapping and understanding the Earth’s geography. They provide a standardized system for representing locations, facilitating communication and collaboration across different disciplines.
Understanding the Importance of Latitude:
The study of lines of latitude offers a deeper understanding of our planet’s geography, climate, and even the passage of time. By grasping the concept of latitude, we gain a broader perspective on how Earth’s position in space influences various aspects of our world. This knowledge is vital for understanding global patterns, predicting weather, and navigating our planet effectively.
FAQs about Lines of Latitude:
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude and longitude are two key elements of a coordinate system used to pinpoint locations on Earth. Latitude refers to the angular distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees. Longitude, on the other hand, refers to the angular distance east or west of the prime meridian, also measured in degrees.
Q: How are lines of latitude used in everyday life?
A: Lines of latitude are crucial for various aspects of our daily lives. They are used in navigation, weather forecasting, climate modeling, and even in the design of maps and atlases. They help us understand the Earth’s geography, climate patterns, and the distribution of various resources.
Q: Are lines of latitude always perfectly straight?
A: While lines of latitude are often depicted as straight lines on maps, they are actually circles that run parallel to the equator. However, due to the Earth’s curvature, these circles appear as curved lines on flat maps, especially at higher latitudes.
Q: Why are some lines of latitude more important than others?
A: All lines of latitude are important in their own way, as they contribute to a complete understanding of the Earth’s geography. However, some lines of latitude hold special significance. For example, the equator is a fundamental line that divides the Earth into hemispheres and plays a crucial role in climate patterns. Other important lines include the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, which mark the boundaries of the tropical zones.
Tips for Understanding Lines of Latitude:
- Visualize: Imagine the Earth as a sphere and visualize the equator as a circle passing through the middle of the sphere. Then, imagine other circles parallel to the equator, extending from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- Use a globe: A globe provides a more accurate representation of the Earth’s curvature and helps you understand how lines of latitude are actually circles.
- Study maps: Examine maps and atlases to familiarize yourself with the location and significance of different lines of latitude.
- Explore online resources: There are numerous online resources and interactive tools that can help you learn more about latitude and longitude.
Conclusion:
Lines of latitude are fundamental to our understanding of the Earth’s geography, climate, and even the passage of time. They provide a framework for locating places, predicting weather patterns, and navigating our planet effectively. By grasping the concept of latitude, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our world and the profound influence of Earth’s position in space on various aspects of our lives.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Grid: Understanding Lines of Latitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!