Navigating the Landscape of Montana: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Montana: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Montana: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Montana: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data
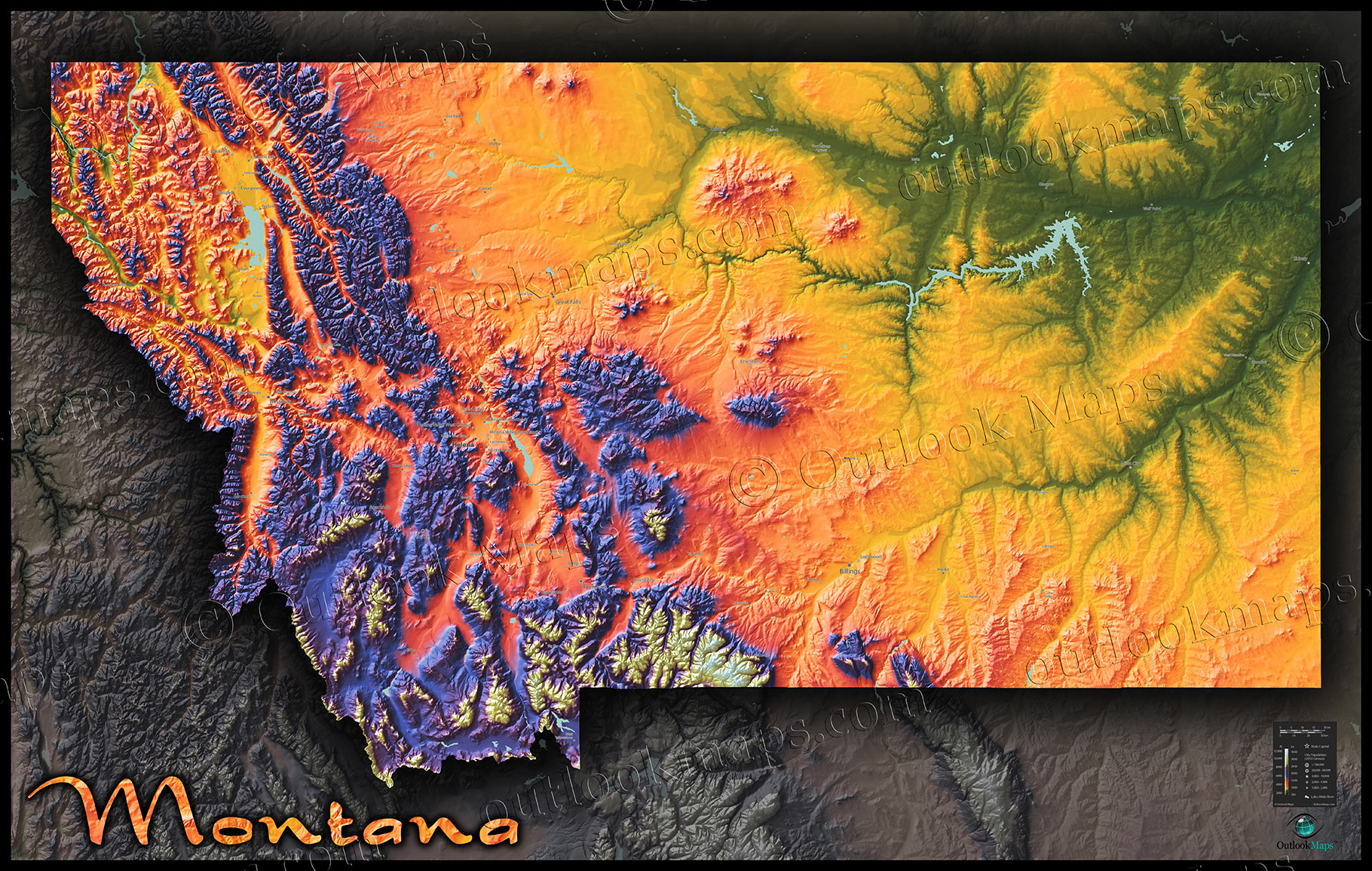
The state of Montana, with its vast expanse of rugged mountains, pristine lakes, and sprawling plains, offers a unique and captivating landscape. Understanding this terrain, its features, and its complexities is crucial for diverse stakeholders, ranging from outdoor enthusiasts and researchers to government agencies and businesses. This guide delves into the importance of accessing and utilizing geographic data, commonly known as "map Montana requests," to navigate this intricate landscape effectively.
The Significance of Geographic Data
Geographic data, often visualized through maps, provides a foundation for informed decision-making across various sectors. In Montana, the significance of this data becomes even more pronounced due to the state’s unique geographical features and diverse industries.
- Environmental Management: Understanding the distribution of natural resources, identifying areas prone to natural disasters like wildfires or floods, and monitoring environmental changes all rely heavily on accurate and up-to-date geographic data.
- Infrastructure Development: Planning and constructing roads, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects require precise mapping of terrain, land ownership, and existing infrastructure.
- Tourism and Recreation: Mapping trail systems, identifying scenic viewpoints, and understanding the accessibility of outdoor recreation areas are essential for attracting tourists and supporting the tourism industry.
- Agriculture and Land Management: Farmers and ranchers utilize geographic data to monitor soil conditions, optimize irrigation systems, and manage livestock grazing patterns.
- Emergency Response: First responders rely on maps to navigate quickly and efficiently during emergencies, locate potential hazards, and coordinate rescue efforts.
Accessing Geographic Data: The "Map Montana Request" Process
Obtaining geographic data for Montana can be accomplished through various channels, each with its own specific procedures and requirements. The process of accessing this data, often referred to as a "map Montana request," involves several key steps:
1. Identifying the Data Needs:
- Define the specific purpose of the request: Clearly articulate the intended use of the geographic data. Is it for research, planning, or operational purposes?
- Identify the geographic area of interest: Define the specific region of Montana that needs to be mapped.
- Determine the required data types: Specify the specific geographic information needed, such as elevation data, land cover types, or infrastructure details.
2. Selecting the Data Source:
- Government Agencies: Montana agencies like the Department of Natural Resources and Conservation, the Department of Transportation, and the Department of Environmental Quality offer various geographic data sets.
- Private Organizations: Companies specializing in geographic data collection and analysis often provide comprehensive data sets for Montana.
- Open Data Platforms: Publicly available data platforms like the National Map or the USGS EarthExplorer offer free access to a wide range of geographic information.
3. Submitting the Request:
- Contact the relevant data provider: Reach out to the agency or organization holding the desired data.
- Provide detailed information about the request: Include the purpose, geographic area, data types, and any specific requirements.
- Follow the established procedures: Each data provider has its own specific guidelines for submitting requests.
4. Data Acquisition and Processing:
- Data Download or Access: Depending on the provider and data format, the data may be downloaded directly or accessed through a web interface.
- Data Processing: The acquired data may require processing, such as converting formats, cleaning inaccuracies, or integrating with other data sets.
5. Utilizing the Data:
- Visualization and Analysis: The processed data can be used to create maps, charts, and other visual representations to analyze patterns, trends, and relationships.
- Decision-Making: The insights gained from the data can inform decision-making processes in various sectors, from land use planning to disaster preparedness.
FAQs: Navigating the "Map Montana Request" Landscape
Q: What are the most common types of geographic data available for Montana?
A: Common data types include:
- Elevation Data: Digital elevation models (DEMs) provide detailed information about the elevation of the terrain, crucial for understanding topography and slope.
- Land Cover Data: Maps depicting the different land cover types, such as forests, grasslands, water bodies, and urban areas, are essential for resource management and environmental analysis.
- Infrastructure Data: Maps showing the location of roads, bridges, pipelines, power lines, and other infrastructure are vital for planning and development.
- Hydrologic Data: Information on rivers, streams, lakes, and groundwater resources is essential for water resource management, flood control, and irrigation planning.
- Soil Data: Maps depicting soil types, fertility, and other characteristics are valuable for agricultural planning and land management.
Q: Are there any limitations or restrictions on accessing geographic data in Montana?
A: Some data sets may be subject to limitations or restrictions, such as:
- Confidentiality: Data containing sensitive information, like private property boundaries or confidential business data, may be restricted.
- Copyright: Data produced by private companies may be subject to copyright protection, requiring permission for use.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy and reliability of data sets can vary depending on the source and collection methods.
Q: What are the potential benefits of utilizing geographic data in Montana?
A: The benefits of utilizing geographic data in Montana are numerous and far-reaching:
- Improved Decision-Making: Geographic data provides a foundation for informed decisions across various sectors, from land use planning to disaster preparedness.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Geographic data can optimize resource allocation, streamline operations, and reduce costs by providing spatial insights.
- Increased Safety: Maps and geographic data can help mitigate risks, improve emergency response, and enhance public safety.
- Environmental Stewardship: Geographic data aids in understanding environmental changes, managing natural resources, and promoting sustainable practices.
- Economic Growth: Geographic data supports economic development by enabling informed investment decisions, promoting tourism, and fostering innovation.
Tips for Success: Maximizing the Value of "Map Montana Requests"
- Clearly Define Your Needs: Before submitting a request, carefully define your specific requirements, including the purpose, geographic area, data types, and format preferences.
- Research Available Data Sources: Explore multiple sources of geographic data to find the most comprehensive and accurate information.
- Contact Data Providers Directly: Reach out to the relevant agencies or organizations to inquire about specific data sets, availability, and access procedures.
- Understand Data Limitations: Be aware of potential limitations, such as data accuracy, confidentiality, and copyright restrictions.
- Utilize Data Visualization Tools: Employ mapping software and other visualization tools to analyze the data and extract meaningful insights.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Geographic Data
Accessing and utilizing geographic data, often referred to as "map Montana requests," is crucial for understanding and navigating the complex landscape of Montana. By leveraging this data, various stakeholders can make informed decisions, optimize resource management, promote economic development, and protect the environment. As technology continues to advance, the availability and accessibility of geographic data will continue to grow, empowering individuals and organizations to make informed decisions and navigate the landscape of Montana with greater clarity and confidence.

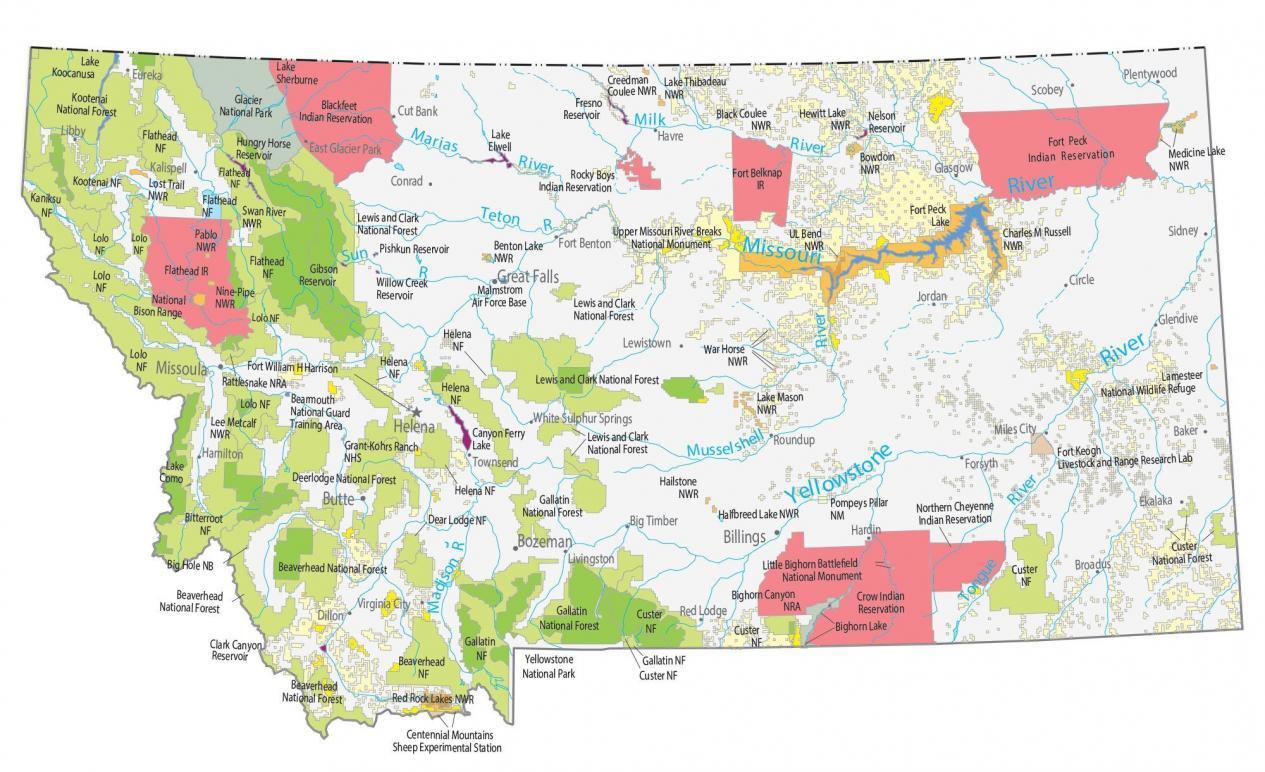

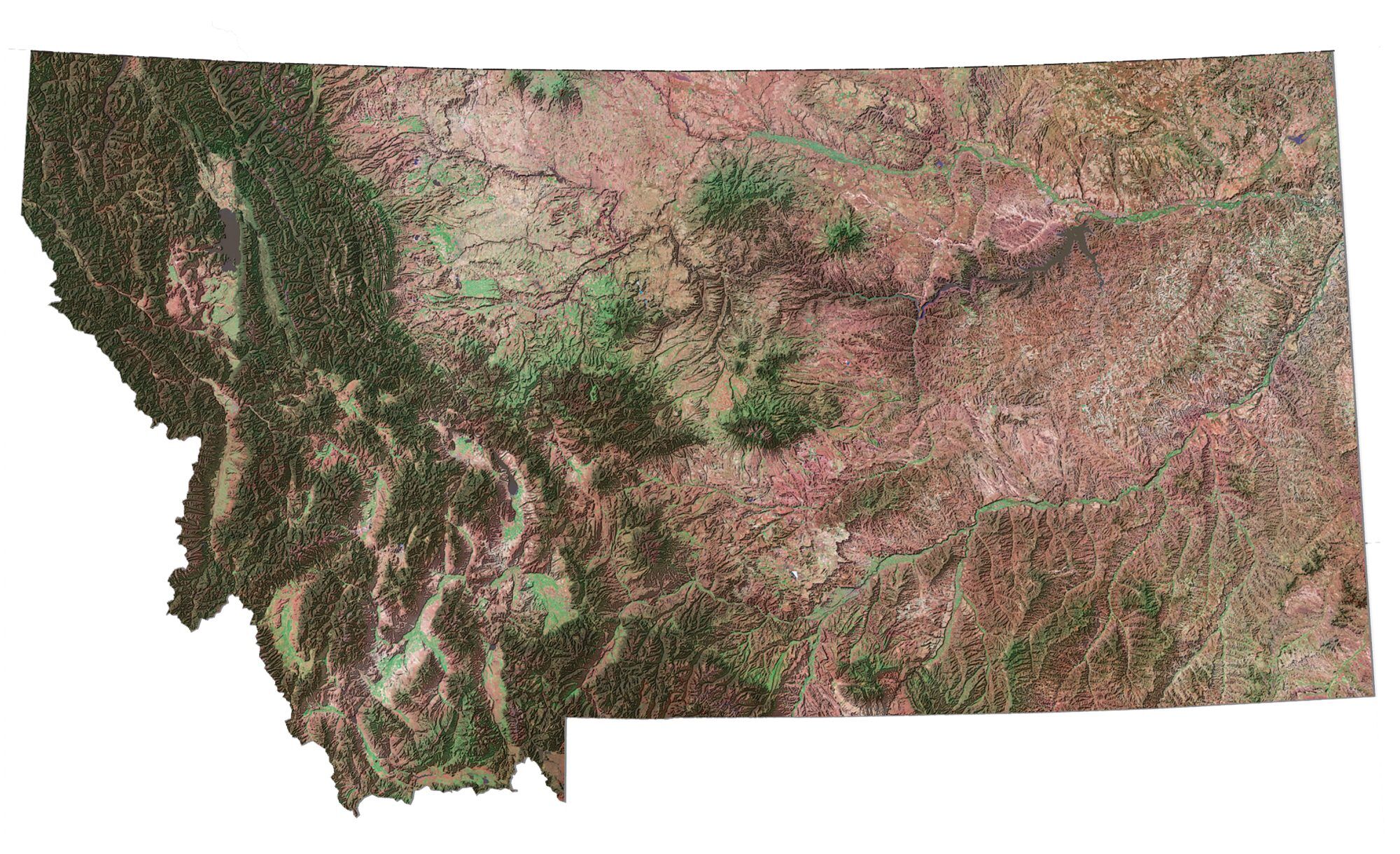




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Montana: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Geographic Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!