Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Zip Code Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Zip Code Mapping
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Zip Code Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Zip Code Mapping
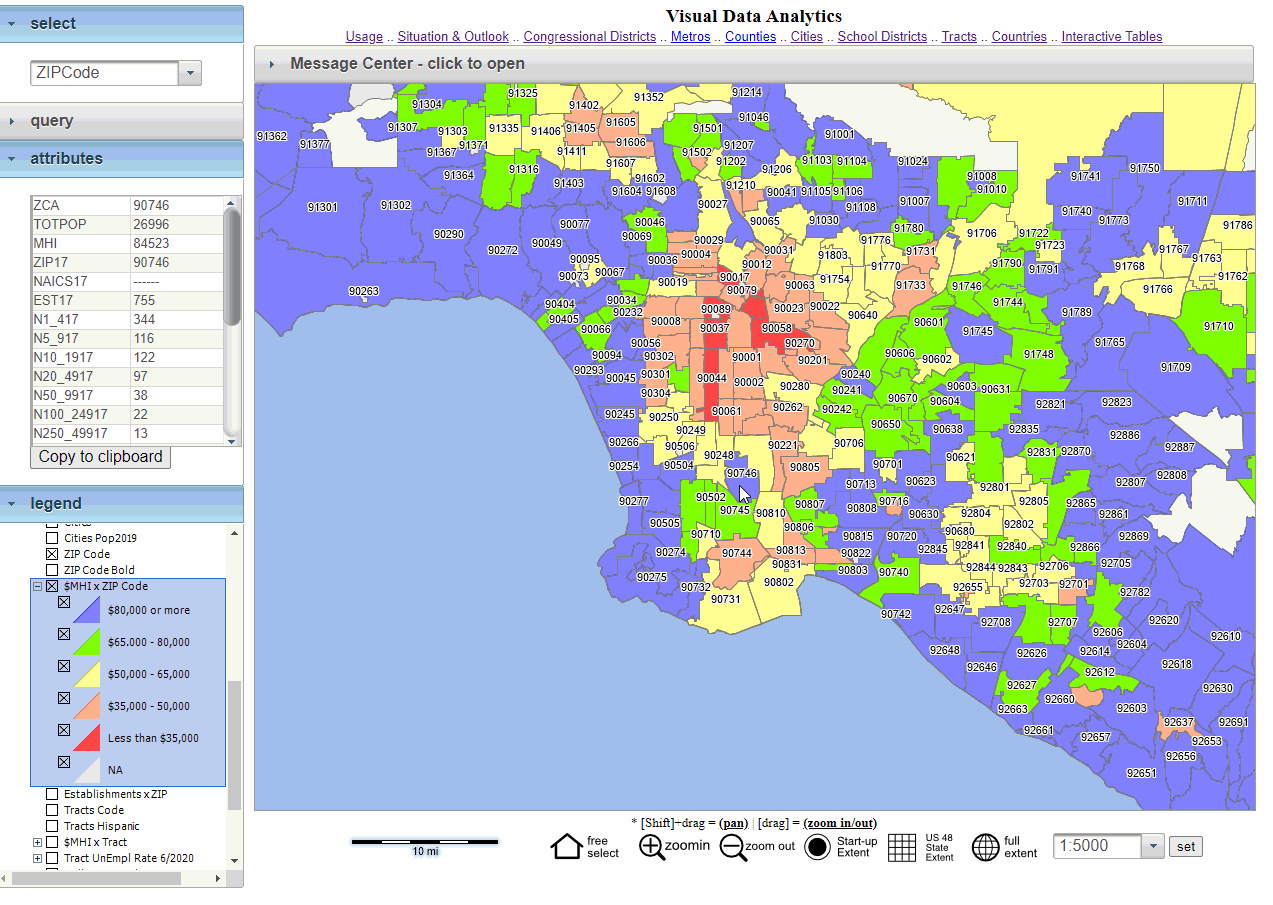
The seemingly simple act of assigning a numerical code to a geographic area has revolutionized our understanding and interaction with the world. Zip codes, those five-digit numerical identifiers, serve as the bedrock for efficient mail delivery, but their impact extends far beyond the realm of postal services. They are the invisible threads that weave together diverse data sets, facilitating a deeper understanding of demographic trends, economic activity, and even the spread of disease.
The Evolution of Zip Codes: From Postal Efficiency to Data Infrastructure
The genesis of zip codes can be traced back to 1963 when the United States Postal Service (USPS) introduced the system to streamline mail delivery. By grouping addresses into smaller, more manageable zones, the USPS significantly improved efficiency and reduced delivery times. However, the potential of zip codes as a powerful data tool was soon recognized.
As the digital age dawned, zip codes became a vital component of geographic information systems (GIS). GIS utilizes spatial data to create maps and analyze geographic patterns. With zip codes as a foundational element, GIS platforms could integrate data from various sources, such as census data, economic indicators, and health records, to paint a comprehensive picture of a region.
Harnessing the Power of Zip Code Mapping: A Multifaceted Tool for Insight and Action
The applications of zip code mapping are as diverse as the data itself. Here are a few examples:
-
Demographic Analysis: Zip codes provide a granular level of insight into population demographics. By analyzing data associated with specific zip codes, researchers can identify population density, age distribution, income levels, and other critical demographic characteristics. This information is invaluable for businesses seeking to target specific customer segments, for urban planners seeking to optimize resource allocation, and for social scientists studying population trends.
-
Economic Development: Understanding the economic landscape of a region is crucial for businesses, investors, and policymakers. Zip code mapping allows for the analysis of economic activity within specific geographic areas. By overlaying data on business density, employment rates, and income levels, researchers can identify areas with high economic potential or areas facing economic challenges. This data can inform investment decisions, guide economic development strategies, and support targeted interventions.
-
Public Health: Public health professionals rely heavily on zip code mapping to understand the spread of diseases, identify areas with high rates of specific health conditions, and target public health initiatives. By analyzing health data associated with specific zip codes, researchers can identify patterns of disease incidence, risk factors, and access to healthcare services. This information helps to prioritize public health interventions, allocate resources effectively, and improve the overall health of a community.
-
Environmental Studies: Zip codes are increasingly used in environmental research to study the impact of environmental factors on human health and well-being. By mapping environmental data such as air quality, water quality, and proximity to hazardous waste sites, researchers can identify areas with elevated environmental risks. This information can guide environmental policy, inform land use decisions, and promote sustainable development practices.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Applications of Zip Code Mapping
The utility of zip code mapping extends beyond traditional applications. Here are some emerging trends:
-
Spatial Analysis: With the advent of advanced spatial analysis techniques, zip codes are now used to analyze complex spatial relationships and patterns. For example, by analyzing the spatial distribution of businesses, researchers can identify clusters of similar businesses, understand competition dynamics, and identify potential market opportunities.
-
Predictive Modeling: By combining zip code data with other data sources, researchers can build predictive models to forecast future trends. For example, by analyzing historical crime data associated with specific zip codes, researchers can develop models to predict areas with a high risk of crime. This information can help law enforcement agencies allocate resources effectively and implement targeted crime prevention strategies.
-
Citizen Engagement: Zip code mapping is becoming a valuable tool for citizen engagement. By mapping local issues and concerns, communities can identify areas of need, prioritize projects, and advocate for change. For example, residents can use zip code mapping to track the location of potholes, identify areas with inadequate street lighting, or map the availability of public transportation.
Addressing the Challenges of Zip Code Mapping
Despite the numerous benefits, zip code mapping is not without its limitations. Here are some key challenges:
-
Data Quality: The accuracy and completeness of zip code data are crucial for reliable analysis. However, data quality can vary depending on the source, and inconsistencies can arise due to changes in boundaries, address updates, and data collection errors.
-
Privacy Concerns: As zip codes are often linked to personal information, there are concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to ensure that data is anonymized and used responsibly to protect the privacy of individuals.
-
Spatial Resolution: Zip codes are relatively large geographic units, and they may not always capture the fine-grained spatial variations that are important for specific research questions.
-
Dynamic Boundaries: Zip code boundaries are not static and can change over time, which can complicate data analysis and interpretation.
Navigating the Future of Zip Code Mapping
Despite the challenges, zip code mapping remains a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the complexities of the modern world. As technology advances and data sources become more sophisticated, the potential of zip code mapping will continue to grow.
By addressing the limitations and ensuring responsible data use, zip code mapping can continue to serve as a valuable resource for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. The ability to harness the power of data to understand and respond to the challenges and opportunities of our time is crucial, and zip code mapping plays a vital role in this process.
FAQs by Map Maker with Zip Codes
Q: What are the benefits of using zip codes in mapping?
A: Zip codes offer several benefits for mapping:
- Granularity: They provide a finer level of geographic detail compared to larger administrative units, allowing for more localized analysis.
- Standardization: Their consistent structure across the country ensures data compatibility and simplifies data integration.
- Accessibility: Zip codes are readily available in various data sources, making them easily accessible for mapping purposes.
- Data Linkage: They facilitate linking geographic data with other datasets, such as demographic, economic, and health data.
Q: How can zip codes be used for business analysis?
A: Zip codes are valuable for businesses seeking to understand their target market, optimize marketing campaigns, and make informed location decisions. They can be used to:
- Identify customer demographics: By analyzing zip code-based demographic data, businesses can gain insights into their customer base and tailor marketing strategies accordingly.
- Analyze market potential: Businesses can assess the potential of different geographic areas based on factors like income levels, consumer spending patterns, and business density.
- Locate new businesses: Zip code mapping helps identify areas with high customer density and low competition, facilitating strategic location choices.
Q: What are some challenges associated with using zip codes in mapping?
A: While zip codes offer many benefits, there are also some challenges:
- Data Accuracy: Inaccurate or outdated zip code data can lead to errors in analysis and mapping.
- Privacy Concerns: Linking personal information to zip codes raises privacy concerns, requiring careful data handling practices.
- Spatial Resolution: Zip codes are relatively large units, potentially masking finer-grained spatial variations relevant to specific research questions.
- Dynamic Boundaries: Changing zip code boundaries can complicate data analysis and interpretation over time.
Q: How can I access zip code data for mapping purposes?
A: Several sources provide access to zip code data:
- United States Postal Service (USPS): The USPS offers zip code data and tools for mapping and address validation.
- U.S. Census Bureau: The Census Bureau provides detailed demographic and socioeconomic data linked to zip codes.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Platforms: Many GIS platforms, such as ArcGIS and QGIS, offer built-in zip code data and tools for mapping.
- Third-Party Data Providers: Numerous private companies specialize in providing comprehensive geographic data, including zip code information.
Tips by Map Maker with Zip Codes
- Validate Data: Always verify the accuracy and completeness of zip code data before using it for analysis or mapping.
- Consider Data Sources: Choose data sources carefully, ensuring they meet your specific needs and data quality standards.
- Address Privacy Concerns: Employ appropriate data anonymization techniques and follow ethical guidelines when using zip code data linked to personal information.
- Utilize Advanced Mapping Tools: Explore advanced GIS software and tools to enhance mapping capabilities and conduct complex spatial analysis.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on changes in zip code boundaries and data availability to ensure the accuracy of your mapping projects.
Conclusion by Map Maker with Zip Codes
Zip codes, once solely a tool for efficient mail delivery, have evolved into a powerful data infrastructure underpinning a wide range of applications. From demographic analysis to public health interventions and economic development strategies, zip code mapping plays a crucial role in understanding and navigating the complexities of our world. By harnessing the power of data and addressing the challenges associated with zip code mapping, we can unlock new insights, inform better decisions, and create a more informed and equitable society.
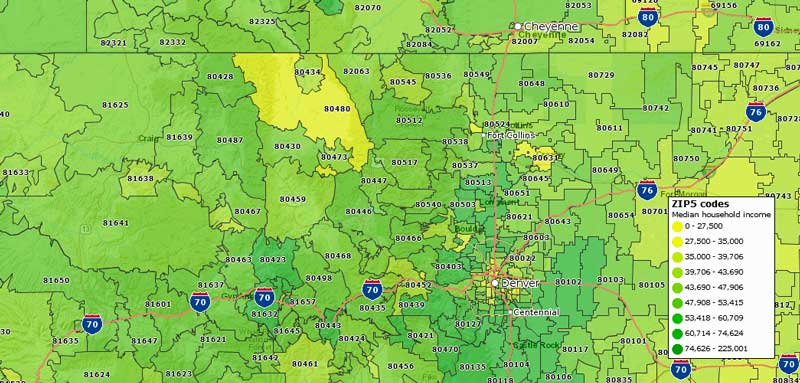

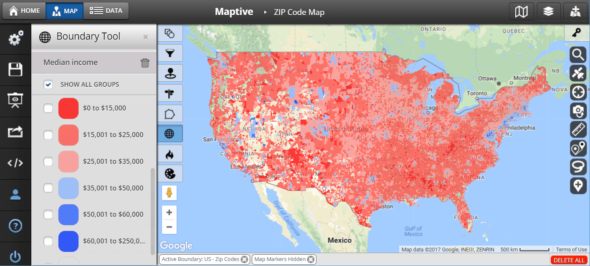



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: The Importance of Zip Code Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!