Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Makers
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Makers
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Makers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Makers
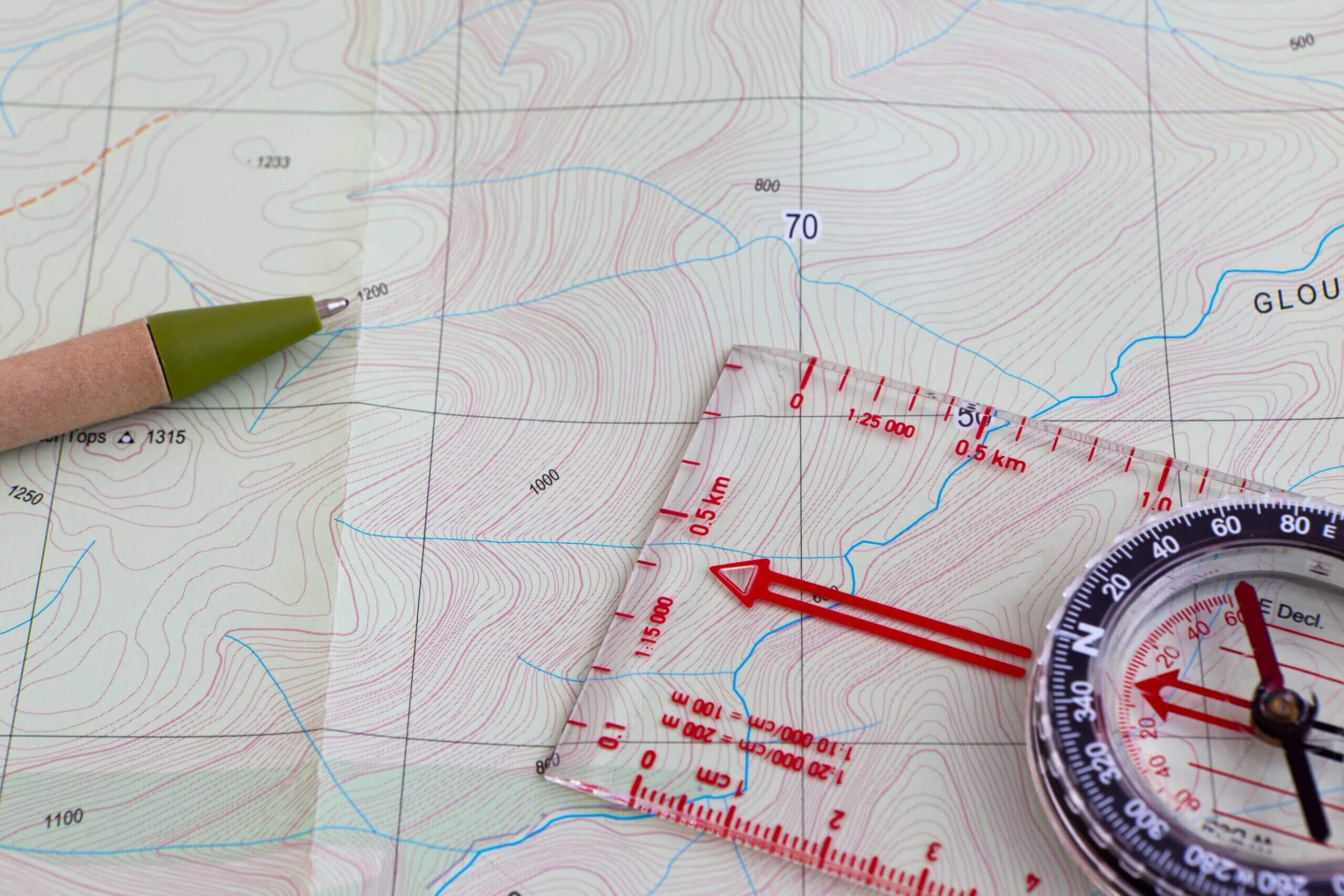

Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and contour markings, offer a unique window into the Earth’s surface. They provide a detailed representation of terrain, revealing elevation changes, valleys, hills, and other features that shape our landscapes. While these maps have long been essential for surveyors, hikers, and outdoor enthusiasts, the advent of digital technology has revolutionized their creation and accessibility.
Understanding Topographic Map Makers: Tools for Visualization and Exploration
Topographic map makers, also known as topographic mapping software or tools, are digital applications that enable users to create, edit, and analyze topographic maps. These tools leverage sophisticated algorithms and datasets to translate raw elevation data into visually compelling and informative representations of the terrain.
The Core Functionalities of Topographic Map Makers:
- Elevation Data Processing: These tools ingest and process elevation data from various sources, including LiDAR scans, aerial imagery, and digital elevation models (DEMs). This data is then transformed into a grid of elevation points, forming the foundation for the map.
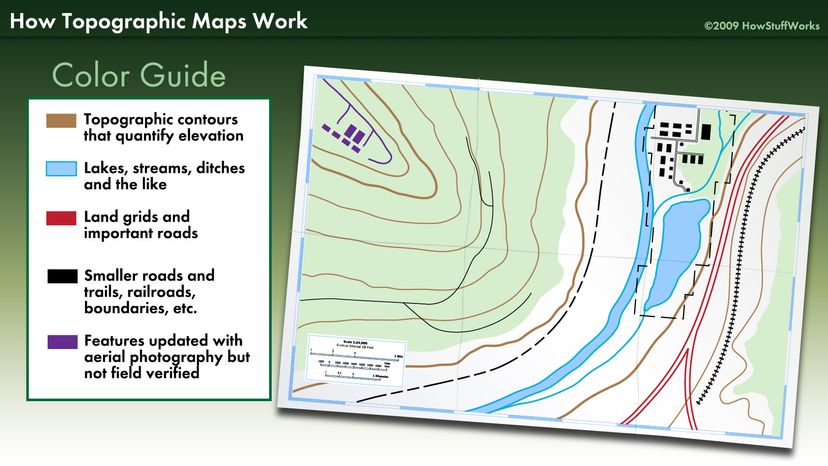
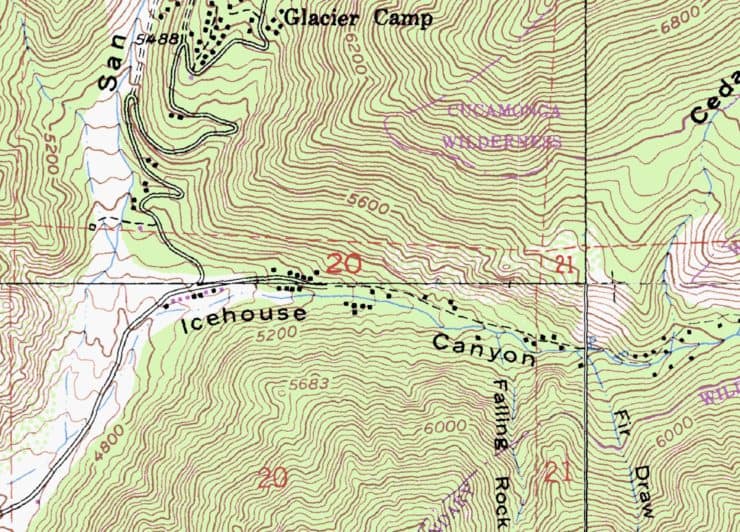
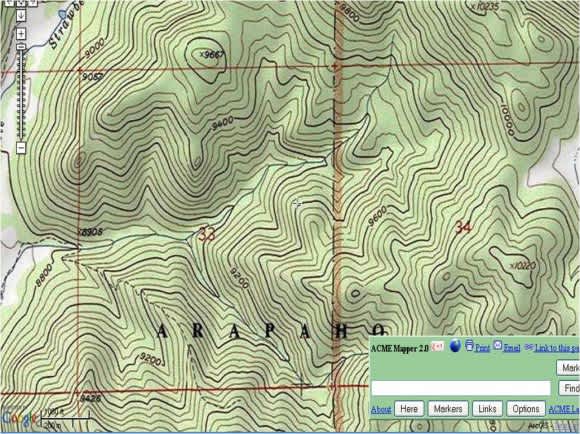
- Contour Line Generation: The software automatically generates contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. These lines, often depicted as brown lines on the map, provide a clear visual representation of the terrain’s slopes and changes in elevation.
- Map Visualization and Styling: Users can customize the appearance of their maps, choosing from a variety of map projections, color palettes, and symbology to highlight specific features and enhance readability.
- Data Analysis and Integration: Many topographic map makers offer advanced analytical capabilities, allowing users to calculate slope gradients, determine watershed boundaries, analyze terrain profiles, and integrate other geospatial data, such as land cover information, into their maps.
- Output Formats: The generated maps can be exported in various formats, including common image files (JPEG, PNG) and geospatial data formats (shapefiles, GeoTIFF), ensuring compatibility with other mapping and GIS applications.
The Benefits of Using Topographic Map Makers:
- Improved Visualization: Topographic maps provide a clear and concise representation of terrain, facilitating a deeper understanding of the landscape’s physical characteristics. This is particularly valuable for planning outdoor activities, assessing environmental impacts, and making informed decisions about land use.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By integrating elevation data with other relevant data layers, topographic map makers enable users to analyze terrain features in conjunction with factors like vegetation, soil type, and infrastructure. This comprehensive approach supports informed decision-making in various fields, including construction, agriculture, and disaster management.
- Increased Accessibility: Digital topographic map makers have democratized map creation, making it accessible to a wider audience. Users without specialized training can now easily generate high-quality maps, leveraging readily available elevation data and intuitive software interfaces.
- Streamlined Workflow: The automation features of these tools streamline the map creation process, reducing the time and effort required for manual cartographic work. This efficiency allows users to focus on data analysis and interpretation, maximizing the value of topographic data.
Exploring the Diverse Applications of Topographic Map Makers:
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps for planning routes, assessing trail difficulty, and identifying potential hazards. These maps provide crucial information about elevation changes, terrain features, and water sources, ensuring safer and more enjoyable experiences.
- Land Management and Planning: Government agencies, environmental organizations, and developers utilize topographic maps for land use planning, habitat mapping, and natural resource management. These maps help visualize terrain features, identify potential development constraints, and assess the impact of proposed projects on the environment.
- Construction and Engineering: Topographic maps are essential for civil engineering projects, providing critical data for site surveys, road design, and construction planning. They help engineers assess the feasibility of projects, minimize environmental impact, and ensure safe and efficient construction.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Management: In disaster scenarios, topographic maps provide crucial information about terrain, access routes, and potential hazards. This data supports rescue efforts, emergency planning, and post-disaster recovery operations.
- Scientific Research: Researchers in various fields, including geology, ecology, and climate science, use topographic maps to analyze terrain features, understand landscape evolution, and study the impact of environmental changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Topographic Map Makers:
Q1: What types of elevation data can be used with topographic map makers?
A: Topographic map makers can utilize a variety of elevation data sources, including:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed elevation models, often with high accuracy and resolution.
- Aerial Imagery: Orthophotos and aerial photographs can be processed to extract elevation information, particularly for areas with limited LiDAR coverage.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are digital representations of elevation data, often derived from multiple sources and available in various resolutions and formats.
Q2: How can I access elevation data for my area of interest?
A: Several sources provide free and paid access to elevation data:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS offers a wide range of DEMs, including the National Elevation Dataset (NED) and the 3DEP project, covering the entire United States.
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): NOAA provides access to bathymetric data, which maps ocean floor depths.
- European Space Agency (ESA): ESA offers global elevation data from its Copernicus program, including the Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM).
- Commercial Data Providers: Companies like Esri, Mapbox, and DigitalGlobe offer high-resolution elevation data and mapping services.
Q3: What are the key features to consider when choosing a topographic map maker?
A: When selecting a topographic map maker, consider the following features:
- Data Sources and Formats: Ensure the software supports the elevation data formats you plan to use.
- Contour Line Generation: Evaluate the software’s ability to generate accurate and visually appealing contour lines.
- Map Visualization and Customization: Look for options to customize the map’s appearance, including projections, color palettes, and symbology.
- Data Analysis and Integration: Consider the software’s capabilities for slope analysis, watershed delineation, and integrating other geospatial data.
- Output Formats: Ensure the software can export maps in desired formats, including image files and geospatial data formats.
- User Interface and Ease of Use: Choose software with an intuitive interface and user-friendly features.
- Cost and Licensing: Determine the software’s pricing model and licensing terms.
Tips for Effective Use of Topographic Map Makers:
- Understand the Data: Before using topographic map makers, familiarize yourself with the source, accuracy, and resolution of the elevation data you are using.
- Choose Appropriate Projections: Select map projections that minimize distortion and accurately represent the terrain for your area of interest.
- Optimize Contour Line Density: Adjust the contour interval to match the scale and complexity of the terrain, ensuring clear visualization without overwhelming the map.
- Experiment with Symbology and Color Palettes: Use different colors and symbols to highlight specific features and enhance the map’s readability.
- Integrate Additional Data: Combine topographic data with other geospatial information, such as land cover, infrastructure, and population density, to create comprehensive and informative maps.
Conclusion:
Topographic map makers have transformed the way we create, visualize, and analyze terrain data. These powerful tools offer a wealth of benefits, from enhanced decision-making in various fields to improved visualization and understanding of the Earth’s surface. By leveraging the capabilities of topographic map makers, we can unlock new insights into our landscapes, support informed planning and resource management, and navigate the terrain with greater confidence and precision.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Map Makers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!