Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.2 The Advantages of Embracing Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.3 Applications of Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.4 The Process of Creating Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.5 FAQs about Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Creating Effective Custom Topographic Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation

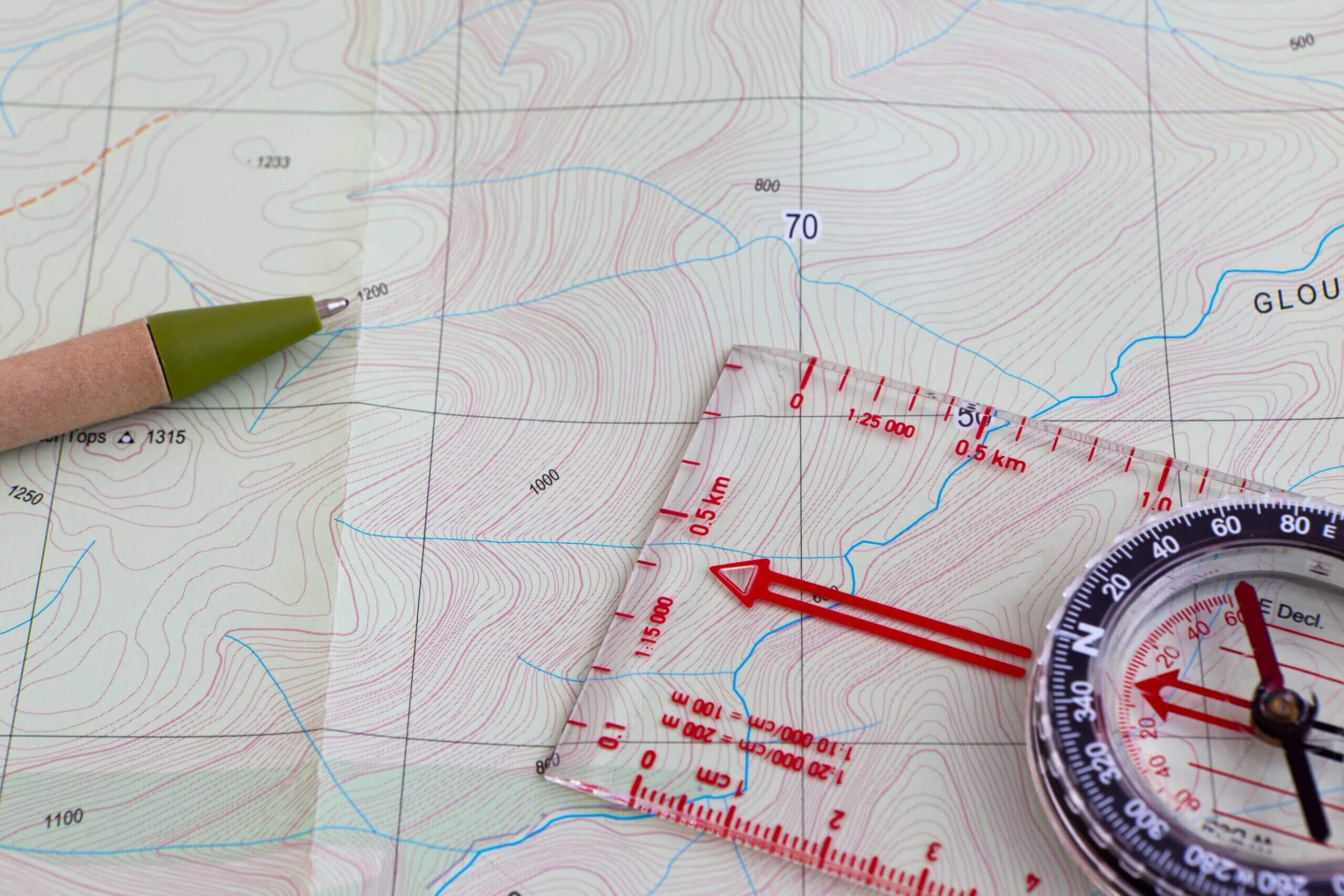
Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and detailed contours, are more than just static representations of the Earth’s surface. They are powerful tools that unlock a deeper understanding of landscapes, revealing hidden features, aiding navigation, and informing crucial decision-making processes. While readily available online resources provide access to pre-made maps, the need for customized topographic maps has steadily grown across diverse fields, ranging from outdoor recreation and land management to scientific research and urban planning.
This article delves into the world of custom topographic map creation, exploring the multifaceted benefits, functionalities, and applications of these personalized cartographic tools.
Understanding the Essence of Custom Topographic Maps
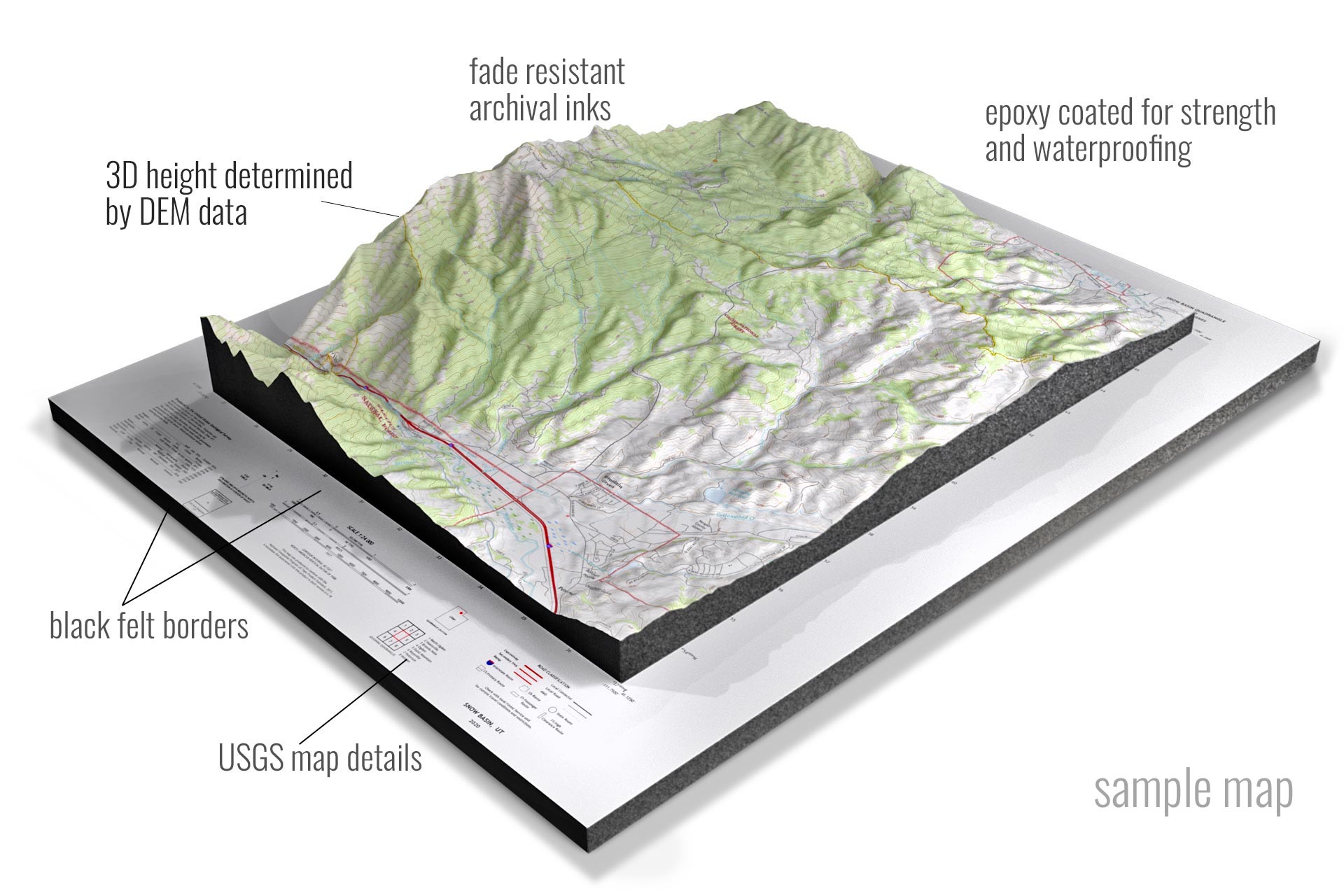
Custom topographic maps, unlike their pre-made counterparts, offer a tailored approach to visualizing and analyzing specific areas of interest. They are crafted to meet precise requirements, incorporating unique data sources, specific scales, and tailored features. This customization allows users to focus on relevant details, enhancing their understanding and facilitating informed decision-making.
The Advantages of Embracing Custom Topographic Maps
The advantages of employing custom topographic maps are multifaceted, extending beyond mere aesthetics. They offer a powerful combination of:
1. Precision and Accuracy: Custom maps are built upon precise data sources, including high-resolution aerial imagery, LiDAR scans, and GPS data. This ensures accurate representation of terrain features, elevations, and other crucial details, fostering confidence in decision-making and analysis.
2. Targeted Focus: Custom maps allow users to define the specific area of interest, focusing on specific details while omitting irrelevant information. This focused approach enhances clarity, simplifies analysis, and facilitates effective communication of key information.
3. Enhanced Visualization: Customized maps provide the flexibility to incorporate specific features and data layers that align with the user’s needs. This includes adding landmarks, trails, elevation profiles, hydrological features, or even custom symbols, enabling a more comprehensive and insightful visual representation of the landscape.
4. Data Integration: Custom maps can integrate diverse data sources, such as geological information, environmental data, or infrastructure details. This integrated approach allows for a holistic view of the landscape, revealing complex relationships and facilitating informed planning and management.
5. Scalability and Flexibility: Custom maps can be tailored to specific scales, accommodating detailed local views or broader regional overviews. They can also be designed in various formats, including print, digital, and interactive versions, catering to diverse needs and applications.
Applications of Custom Topographic Maps
The versatility of custom topographic maps makes them valuable tools in a wide range of fields:
1. Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, mountain bikers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on custom maps to plan routes, identify trails, and assess terrain challenges. Detailed elevation profiles and contour lines provide crucial information for safe and enjoyable adventures.
2. Land Management: Forestry, agriculture, and wildlife management professionals use custom maps to analyze land use, monitor resource availability, and plan sustainable practices. These maps help in identifying areas with specific characteristics, facilitating efficient resource allocation and conservation efforts.
3. Urban Planning: Urban planners utilize custom maps to assess infrastructure needs, analyze development potential, and plan for future growth. Detailed topography, elevation data, and integrated utility networks provide valuable insights for creating sustainable and resilient urban environments.
4. Environmental Studies: Scientists and researchers rely on custom maps for ecological studies, mapping biodiversity hotspots, and analyzing environmental impacts. Detailed topography, hydrological features, and integrated environmental data provide crucial information for understanding complex ecological processes and developing conservation strategies.
5. Construction and Engineering: Civil engineers and construction companies use custom maps to plan infrastructure projects, assess site suitability, and optimize construction processes. Detailed topographic data, including elevation contours and underground utilities, ensure safe and efficient project execution.
6. Disaster Response: Custom maps play a vital role in emergency response, providing real-time situational awareness and aiding in rescue and evacuation efforts. They facilitate communication, resource allocation, and informed decision-making during critical events.
7. Education and Research: Custom maps are valuable teaching tools, enabling students to visualize geographic concepts and explore specific landscapes. Researchers use them to analyze spatial patterns, identify trends, and develop scientific models, contributing to a deeper understanding of the world.
The Process of Creating Custom Topographic Maps
The creation of a custom topographic map involves a multi-step process that ensures accuracy, clarity, and user-specific requirements are met. Here is a general overview:
1. Data Acquisition: This initial step involves gathering relevant data sources, including aerial imagery, LiDAR scans, GPS data, and existing topographic maps. The choice of data sources depends on the specific project requirements and desired level of detail.
2. Data Processing and Analysis: The acquired data is then processed and analyzed to create a digital elevation model (DEM). This model represents the terrain’s elevation values, forming the foundation for the topographic map.
3. Map Design and Layout: The next step involves designing the map’s layout, choosing the appropriate projection, scale, and defining the map’s content. This includes selecting relevant features, such as contour lines, elevation points, landmarks, and custom symbols.
4. Visualization and Rendering: The map is then visualized and rendered using specialized software, incorporating chosen features and data layers. The visual style, including colors, fonts, and symbols, are carefully selected to enhance clarity and communication.
5. Quality Control and Review: The final map undergoes rigorous quality control and review to ensure accuracy, consistency, and adherence to user specifications. This process includes checking data integrity, verifying map features, and ensuring the map meets the project’s intended purpose.
6. Output and Delivery: The completed map is then output in the desired format, including print, digital, or interactive versions. It can be delivered in various file types, allowing for seamless integration with other applications or platforms.
FAQs about Custom Topographic Maps
1. What types of data are used for creating custom topographic maps?
Custom topographic maps utilize a variety of data sources, including:
- Aerial Imagery: High-resolution aerial photographs provide a detailed visual representation of the landscape, capturing terrain features, vegetation, and infrastructure.
- LiDAR Scans: Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) technology uses laser pulses to measure distances and create accurate 3D models of the terrain, capturing detailed elevation data and vegetation information.
- GPS Data: Global Positioning System (GPS) data provides precise location coordinates, used to map trails, boundaries, and other features.
- Existing Topographic Maps: Pre-existing topographic maps serve as a valuable reference, providing existing elevation data and feature information.
2. What is the typical turnaround time for creating a custom topographic map?
The turnaround time for creating a custom topographic map varies depending on the project’s complexity, data availability, and desired level of detail. Simple maps can be completed within a few days, while complex projects may require several weeks.
3. How much does it cost to create a custom topographic map?
The cost of creating a custom topographic map is influenced by various factors, including:
- Project Scope: The size and complexity of the area being mapped, the level of detail required, and the number of features included.
- Data Acquisition: The cost of acquiring necessary data sources, such as aerial imagery or LiDAR scans.
- Map Design and Production: The time and effort involved in designing the map layout, selecting features, and rendering the final product.
4. What are the different output formats available for custom topographic maps?
Custom topographic maps can be delivered in various formats, including:
- Print: High-quality printed maps suitable for field use or presentations.
- Digital: Electronic versions, typically in PDF or image formats, for easy viewing and sharing.
- Interactive: Web-based maps with interactive features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and access additional information.
5. Who can benefit from using custom topographic maps?
Custom topographic maps provide valuable insights and benefits for a wide range of individuals and organizations, including:
- Outdoor enthusiasts: Hikers, mountain bikers, and other outdoor recreationists.
- Land management professionals: Forestry, agriculture, and wildlife management agencies.
- Urban planners and developers: Architects, engineers, and city planners.
- Environmental scientists and researchers: Ecologists, geographers, and environmental consultants.
- Construction and engineering companies: Civil engineers, construction managers, and project developers.
- Emergency response teams: Firefighters, police, and rescue personnel.
- Educators and researchers: Teachers, professors, and students in various disciplines.
Tips for Creating Effective Custom Topographic Maps
1. Define Specific Goals and Objectives: Clearly define the purpose of the map and the specific information it needs to convey. This will guide the selection of data sources, features, and map design elements.
2. Choose the Right Data Sources: Select data sources that provide the necessary level of detail and accuracy for the project. Consider the scale of the map, the terrain’s complexity, and the specific features to be included.
3. Employ a Suitable Map Projection: Choose a map projection that minimizes distortion and accurately represents the area of interest. Consider the geographic location, the map’s scale, and the intended use.
4. Optimize Map Design for Clarity: Design the map layout to ensure clear communication of information. Use a consistent color scheme, legible fonts, and appropriate symbols to enhance readability and visual appeal.
5. Incorporate Relevant Features: Include features that are essential for understanding the landscape and achieving the map’s purpose. This may include contour lines, elevation points, landmarks, trails, boundaries, and other relevant data layers.
6. Consider User Needs and Accessibility: Design the map with the intended audience in mind, ensuring its accessibility and ease of use. Consider the map’s format, scale, and the availability of supporting information.
7. Conduct Thorough Quality Control: Carefully review the final map for accuracy, consistency, and adherence to user specifications. Verify data integrity, check feature accuracy, and ensure the map meets the project’s intended purpose.
Conclusion
Custom topographic maps are powerful tools that offer tailored visualizations and analysis of specific landscapes. Their ability to integrate diverse data sources, provide precise information, and facilitate informed decision-making makes them indispensable across various fields. From outdoor recreation and land management to scientific research and urban planning, custom topographic maps empower users to navigate the terrain, understand complex landscapes, and make informed decisions that shape our world. By embracing the power of customization, we unlock a deeper understanding of our environment and pave the way for informed decisions that benefit both present and future generations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: A Guide to Custom Topographic Map Creation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!