Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Exploration of Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker
Related Articles: Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Exploration of Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Exploration of Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Exploration of Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker

Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker, often referred to as "Map Maker," is an integral part of data visualization and analysis. This lesson introduces students to the powerful tool of mapping data, enabling them to glean insights and communicate complex information in an intuitive and visually compelling manner. The ability to create and interpret maps is not only crucial for understanding spatial relationships, but also for identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within datasets.
Understanding the Essence of Map Maker
At its core, Map Maker is about transforming raw data into meaningful spatial representations. This process involves:
- Data Preparation: Cleaning, organizing, and preparing data for visualization. This may involve standardizing data formats, handling missing values, and ensuring accurate geographic coordinates.
- Map Selection: Choosing the appropriate map projection and basemap to accurately represent the data and geographical context.
- Data Visualization: Representing data visually through various techniques like point markers, heatmaps, choropleth maps, and line graphs, each conveying different types of information.
- Interpretation: Analyzing the resulting map to draw conclusions and identify patterns, trends, and anomalies.
The Importance of Map Maker
The importance of Map Maker lies in its ability to:
- Enhance Understanding: Maps provide a visual representation of data, making it easier to comprehend complex relationships and patterns that might be obscured in tabular form.
- Identify Spatial Patterns: By visualizing data geographically, users can identify clusters, outliers, and spatial trends that might not be evident otherwise.
- Communicate Effectively: Maps are a powerful tool for communicating data-driven insights to a wider audience. They can be used to present research findings, inform decision-making, and raise awareness about important issues.
- Support Decision-Making: Maps can be used to analyze spatial data and inform decisions related to resource allocation, infrastructure development, and public policy.
Exploring the Functionality of Map Maker
Map Maker typically involves the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software, which provides tools for:
- Data Management: Importing, cleaning, and manipulating spatial data.
- Map Creation: Selecting basemaps, defining map projections, and configuring map elements.
- Data Visualization: Applying various visualization techniques to represent data on maps.
- Analysis: Performing spatial analysis tasks such as proximity analysis, overlay analysis, and spatial interpolation.
Benefits of Using Map Maker
The use of Map Maker offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Data Analysis: By visualizing data geographically, users can gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and patterns.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Maps provide valuable insights that can inform strategic decisions in various fields, including urban planning, environmental management, and public health.
- Effective Communication: Maps are a powerful tool for communicating complex data to diverse audiences.
- Increased Efficiency: Map Maker can streamline data analysis and visualization processes, saving time and effort.
FAQs Regarding Map Maker
Q: What types of data can be visualized using Map Maker?
A: Map Maker can be used to visualize a wide range of data types, including:
- Point data: Representing locations such as stores, schools, or crime incidents.
- Line data: Representing linear features such as roads, rivers, or power lines.
- Polygon data: Representing areas such as countries, states, or neighborhoods.
- Raster data: Representing continuous data such as elevation, temperature, or rainfall.
Q: What are the different types of maps that can be created using Map Maker?
A: Map Maker allows for the creation of various map types, including:
- Point maps: Displaying data points on a map.
- Heatmaps: Representing data density using color gradients.
- Choropleth maps: Displaying data values using different colors or shades for different regions.
- Line maps: Representing data along lines, such as population density along a road.
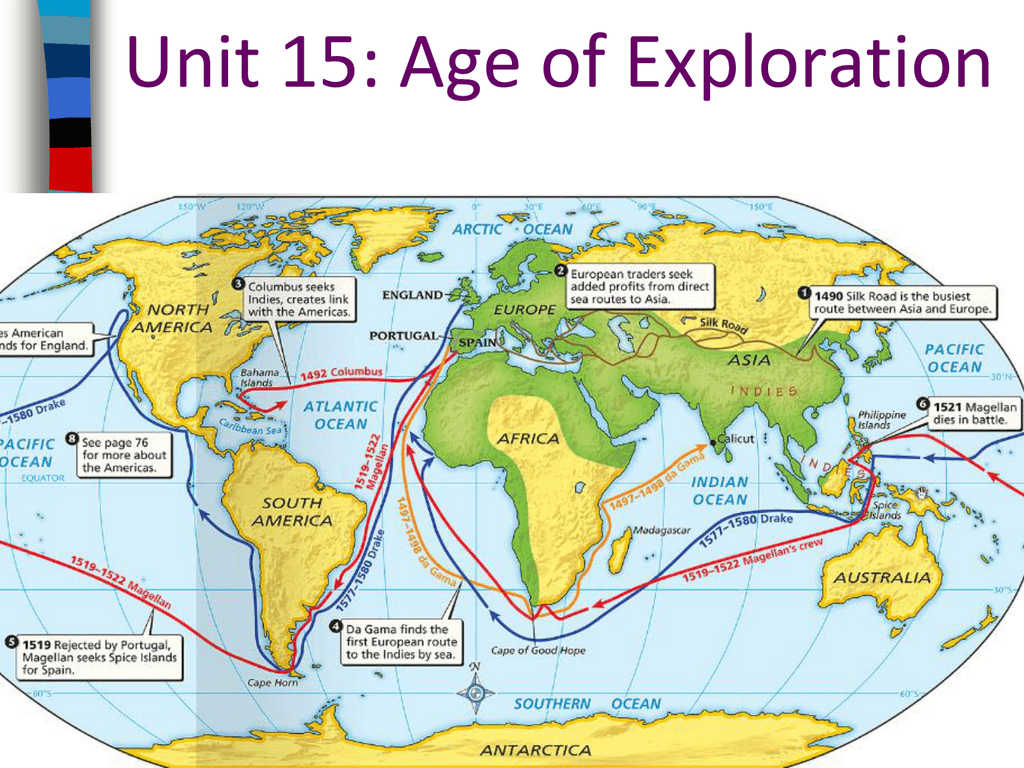
- Flow maps: Displaying movement patterns, such as migration or trade routes.
Q: What are some examples of real-world applications of Map Maker?
A: Map Maker finds applications in diverse fields, including:
- Urban planning: Analyzing population density, transportation networks, and infrastructure needs.
- Environmental management: Monitoring pollution levels, deforestation, and wildlife habitats.
- Public health: Tracking disease outbreaks, identifying health disparities, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Business intelligence: Analyzing customer locations, market trends, and competitor activity.
- Emergency response: Mapping disaster zones, evacuations routes, and resource distribution.
Tips for Using Map Maker Effectively
- Choose the Right Data: Ensure the data is accurate, relevant, and appropriate for the intended purpose.
- Select the Appropriate Map Projection: Consider the geographic area and data characteristics to choose a projection that minimizes distortion.
- Use Clear and Concise Visualizations: Employ colors, symbols, and labels that are easily understandable and visually appealing.
- Provide Context and Interpretation: Include relevant information about the data, map projection, and analysis methods.
- Test and Validate Results: Ensure the map accurately reflects the data and is consistent with expectations.
Conclusion
Map Maker is a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, offering numerous benefits for understanding, communicating, and informing decision-making. By mastering the principles and techniques of Map Maker, individuals can unlock the potential of data to gain insights, solve problems, and make informed decisions. The ability to create and interpret maps is becoming increasingly crucial in a world driven by data, making Map Maker a valuable skill for professionals across various disciplines.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World of Data: A Comprehensive Exploration of Unit 1 Lesson 9: Map Maker. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!