The Art and Science of Cartography: Understanding the Role of the Map Maker
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Cartography: Understanding the Role of the Map Maker
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Cartography: Understanding the Role of the Map Maker. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Cartography: Understanding the Role of the Map Maker

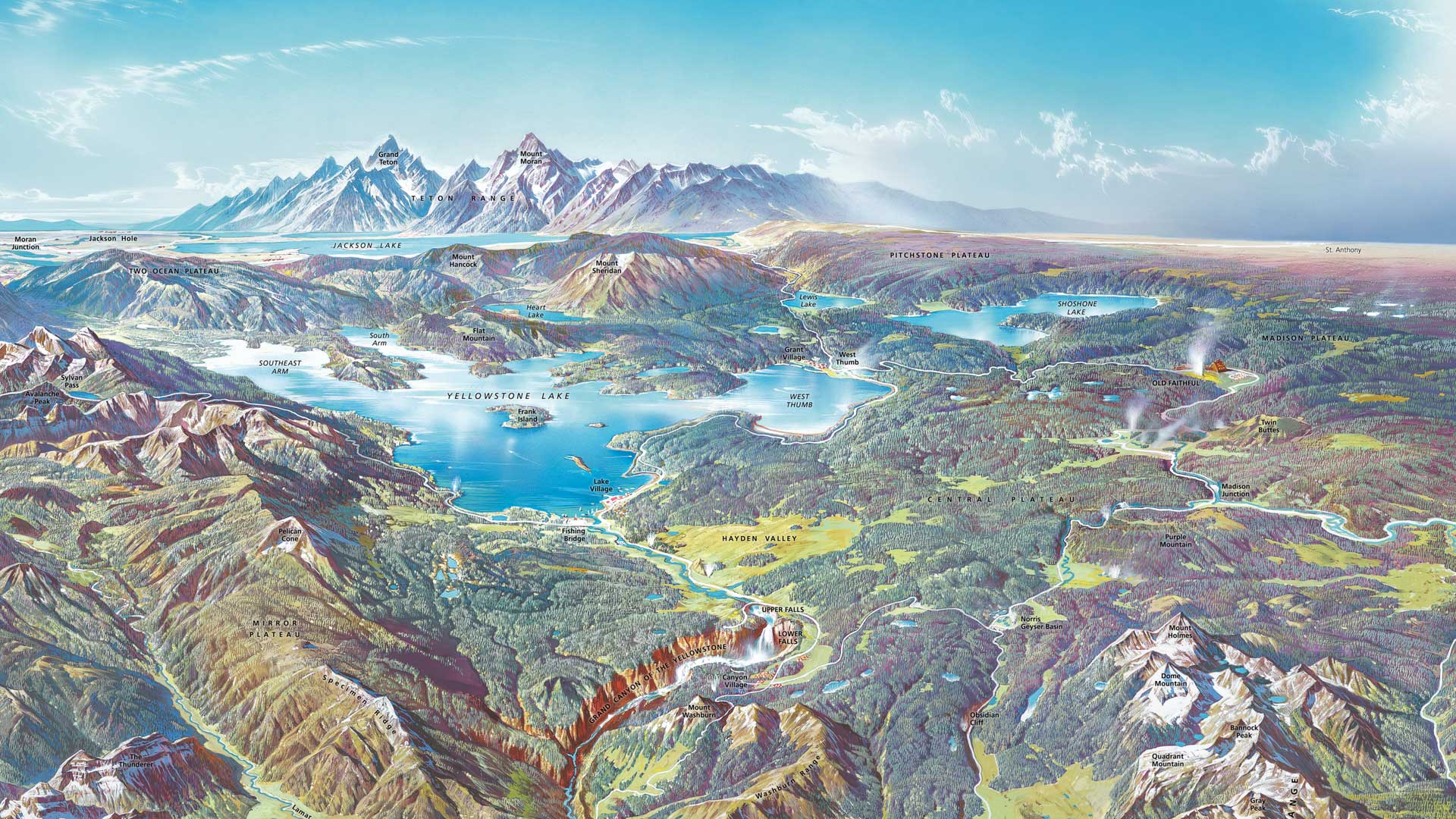
Cartography, the art and science of map making, has been a cornerstone of human civilization for millennia. From ancient cave paintings depicting hunting grounds to intricate nautical charts guiding explorers across vast oceans, maps have played a vital role in our understanding and interaction with the world. The individual responsible for crafting these representations of reality is the map maker.
The title of "map maker" encompasses a wide range of skills and expertise. It transcends the simple act of drawing lines on a piece of paper; it involves a deep understanding of geography, geometry, data analysis, and visual communication. A map maker must possess a keen eye for detail, an ability to synthesize complex information, and a creative flair for presenting data in an accessible and engaging manner.
The Evolution of the Map Maker’s Role
Historically, map makers were often associated with specific professions. Navigators and cartographers created detailed charts for seafaring voyages, while surveyors meticulously mapped land boundaries. However, with the advent of digital technology and the explosion of geographic data, the role of the map maker has evolved significantly.
Today, the map maker is more likely to be a GIS (Geographic Information System) specialist, a data analyst, or a web developer, utilizing sophisticated software and databases to create interactive maps, 3D visualizations, and dynamic geographic representations. This evolution has broadened the scope of map making, encompassing fields such as urban planning, environmental analysis, disaster response, and even social media mapping.
The Importance of the Map Maker’s Work
The work of the map maker has profound implications across various sectors:
- Navigation and Exploration: Maps provide essential guidance for travelers, explorers, and even autonomous vehicles. They facilitate safe and efficient movement across land, sea, and air.
- Urban Planning and Development: Map makers play a crucial role in urban planning, assisting in the development of infrastructure, transportation networks, and public services. They can analyze population density, traffic patterns, and environmental factors to optimize urban design.
- Environmental Management and Conservation: Maps are essential tools for monitoring environmental changes, tracking deforestation, mapping endangered species habitats, and assessing the impact of climate change.
- Disaster Response and Emergency Management: Maps are critical for coordinating rescue efforts, identifying areas of risk, and providing real-time information during natural disasters and emergencies.
- Education and Communication: Maps are powerful tools for teaching geography, history, and culture. They help us visualize complex concepts, understand spatial relationships, and connect with the world around us.
The Challenges Facing Modern Map Makers
Despite the advancements in technology, map makers face unique challenges in the 21st century.
- Data Overload: The vast amount of geographic data available presents a challenge in selecting relevant information and ensuring its accuracy.
- Ethical Considerations: Map makers must be aware of the ethical implications of their work, particularly when dealing with sensitive information such as demographics, crime rates, and political boundaries.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Ensuring that maps are accessible to diverse audiences, including people with disabilities, requires careful consideration of design principles and accessibility standards.
- The Rise of Misinformation: The proliferation of misinformation and "fake news" underscores the importance of accurate and credible map making.
FAQs Regarding Map Making
1. What are the different types of maps?
Maps can be broadly categorized into:
- Reference Maps: These maps provide basic geographic information, such as roads, cities, and landforms. Examples include road maps, topographic maps, and atlases.
- Thematic Maps: These maps focus on a specific theme, such as population density, rainfall patterns, or disease prevalence.
- Navigation Maps: These maps are specifically designed for navigation, including road maps, nautical charts, and aeronautical maps.
- Digital Maps: These maps are created and accessed digitally, often using interactive features and real-time data.
2. What software do map makers use?
Map makers utilize a variety of software tools, including:
- GIS Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are widely used for geospatial analysis, data visualization, and map creation.
- Web Mapping Platforms: Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and Bing Maps offer tools for creating and sharing interactive maps online.
- Graphic Design Software: Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape, and CorelDRAW are used for map design and layout.
3. What are the career paths for map makers?
Map makers can pursue careers in various fields, including:
- GIS Specialist: Analyze spatial data, create maps, and develop geographic information systems.
- Cartographer: Design and produce maps for a variety of purposes, including navigation, planning, and education.
- Data Analyst: Use geographic data to analyze trends, patterns, and relationships.
- Urban Planner: Use maps to plan and design urban environments.
- Environmental Scientist: Use maps to monitor and assess environmental conditions.
Tips for Aspiring Map Makers
- Develop a strong foundation in geography: Gain a comprehensive understanding of geographic concepts, map projections, and spatial data.
- Master GIS software: Become proficient in using GIS software for data analysis, map creation, and visualization.
- Enhance your design skills: Develop strong design skills to create visually appealing and informative maps.
- Stay updated on technological advancements: Continuously learn about new software, tools, and techniques in map making.
- Network with other map makers: Attend conferences, workshops, and online forums to connect with professionals in the field.
Conclusion
The role of the map maker is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for geospatial data. From traditional paper maps to interactive digital visualizations, map makers continue to play a vital role in our understanding and interaction with the world. By leveraging their expertise in geography, data analysis, and visual communication, they provide valuable insights, support informed decision-making, and contribute to a more informed and connected world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Cartography: Understanding the Role of the Map Maker. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!