The Power of Visualization: A Deep Dive into 3D Map Creation
Related Articles: The Power of Visualization: A Deep Dive into 3D Map Creation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visualization: A Deep Dive into 3D Map Creation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visualization: A Deep Dive into 3D Map Creation
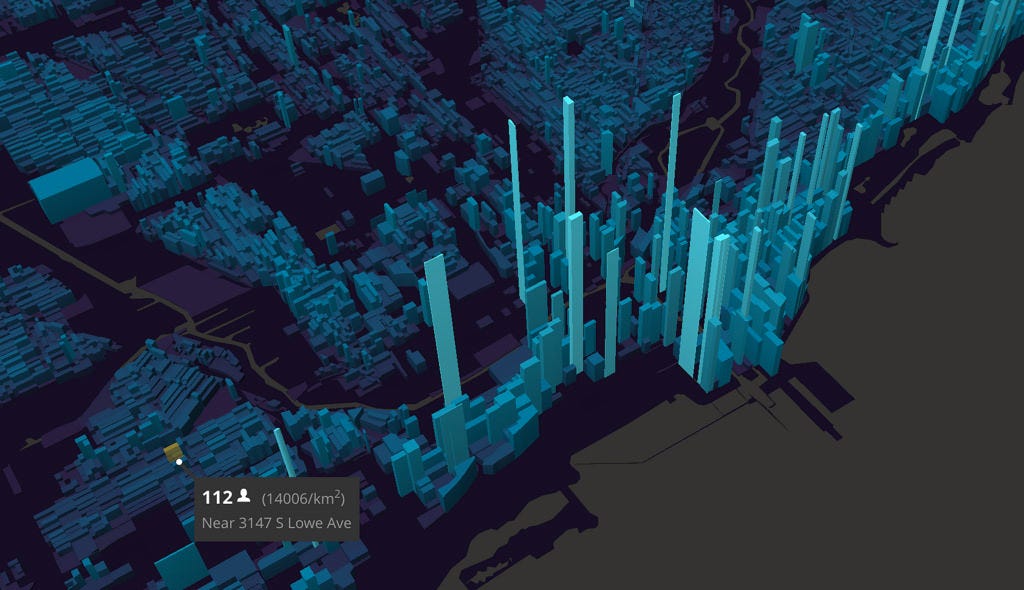
The ability to visualize data is paramount in today’s data-driven world. While traditional two-dimensional maps serve their purpose, the emergence of 3D map creation software has revolutionized the way we understand and interact with spatial information. This technology allows for a more immersive and comprehensive representation of geographic data, offering a wealth of benefits across various fields.
The Evolution of 3D Map Creation
The concept of 3D maps is not new. Early attempts at creating three-dimensional representations of the Earth date back to the 19th century. However, the advent of computer technology in the late 20th century paved the way for the development of sophisticated software capable of generating complex 3D models.
The early stages of 3D map creation were primarily focused on scientific and research applications. However, with advancements in computing power and the widespread adoption of the internet, 3D mapping tools have become more accessible and user-friendly. This accessibility has spurred innovation, leading to the development of a diverse range of applications for 3D maps.
Benefits of 3D Map Creation
The advantages of 3D map creation extend far beyond mere aesthetics. By providing a more comprehensive and interactive representation of spatial data, 3D maps offer a range of benefits across various disciplines:
-
Enhanced Visualization: 3D maps provide a more intuitive and immersive understanding of spatial relationships. Users can easily perceive elevation changes, identify hidden patterns, and gain insights that may be obscured in traditional 2D maps.
-
Improved Data Analysis: By incorporating multiple data layers into a single 3D model, users can analyze complex spatial relationships and identify trends that might not be apparent in isolated datasets. This allows for more informed decision-making in fields like urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
-
Interactive Exploration: 3D maps enable users to explore virtual environments, navigate through complex landscapes, and interact with data in real-time. This interactivity fosters deeper engagement and facilitates a more thorough understanding of the information presented.
-
Increased Accessibility: 3D maps can be readily shared and accessed through various platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and virtual reality headsets. This accessibility allows for wider dissemination of spatial information and promotes collaboration across different stakeholders.
-
Effective Communication: 3D maps provide a powerful tool for communicating complex spatial information to a wider audience. Their visual appeal and interactive nature can effectively convey complex concepts and foster better understanding across diverse backgrounds.
Applications of 3D Map Creation
The applications of 3D map creation are vast and continue to expand as the technology evolves. Some notable examples include:
-
Urban Planning and Development: 3D maps are used to visualize proposed urban developments, assess the impact of infrastructure projects, and optimize city planning strategies.
-
Environmental Monitoring and Management: 3D maps are employed to monitor environmental changes, track natural disasters, and manage natural resources. They help in understanding the impact of climate change, pollution, and deforestation.
-
Resource Exploration and Extraction: 3D maps are used in the exploration and extraction of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals. They provide detailed geological information and facilitate efficient resource management.
-
Transportation and Logistics: 3D maps are used to optimize transportation routes, manage traffic flow, and plan logistics operations. They provide real-time traffic information and assist in navigating complex urban environments.
-
Archaeology and History: 3D maps are used to reconstruct ancient sites, visualize historical events, and preserve cultural heritage. They enable researchers to study past civilizations and understand historical processes.
-
Military and Defense: 3D maps are used for military planning, training, and operations. They provide detailed representations of battlefields, facilitate troop movements, and support tactical decision-making.
-
Education and Training: 3D maps are used in educational settings to teach geography, history, and other subjects in an engaging and interactive manner. They provide immersive learning experiences and enhance student understanding.
-
Gaming and Entertainment: 3D maps are used to create realistic and immersive environments in video games, virtual reality applications, and other forms of entertainment.
Key Features of 3D Map Creation Software
Modern 3D map creation software offers a wide range of features and capabilities, enabling users to create sophisticated and interactive maps. Some key features include:
-
Data Import and Integration: The ability to import and integrate various data sources, including geographic data, imagery, and sensor data.
-
3D Modeling and Visualization: Tools for creating and manipulating 3D models, including terrain, buildings, objects, and other elements.
-
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Functions for analyzing spatial data, identifying patterns, and generating insights.
-
Interactive Exploration and Navigation: Features for exploring and navigating 3D environments, including zooming, panning, and rotating the map.
-
Collaboration and Sharing: Tools for collaborating with others on map projects and sharing maps through various platforms.
-
Customization and Branding: Options for customizing the appearance of maps, including colors, textures, and labels.
FAQs about 3D Map Creation
Q: What types of data can be used to create 3D maps?
A: 3D map creation software can utilize a wide range of data sources, including:
- Geographic data: This includes data from sources like GIS (Geographic Information System), GPS (Global Positioning System), and remote sensing.
- Imagery: Satellite imagery, aerial photography, and other visual data can be used to create realistic 3D models.
- Sensor data: Data collected from sensors, such as weather stations, environmental monitoring devices, and traffic sensors, can be integrated into 3D maps.
- CAD data: Computer-aided design (CAD) data can be used to create detailed 3D models of buildings and infrastructure.
Q: What are the different types of 3D maps?
A: 3D maps can be categorized based on their purpose, data source, and level of detail. Some common types include:
- Terrain maps: These maps focus on representing the topography of an area, including elevation changes, slopes, and landforms.
- Urban maps: These maps showcase the built environment of cities, including buildings, roads, and infrastructure.
- Environmental maps: These maps depict environmental features, such as forests, rivers, and lakes, and may incorporate data on pollution, climate change, and other environmental factors.
- Historical maps: These maps reconstruct past environments and historical events, using archaeological data and historical records.
Q: What are some popular 3D map creation software options?
A: There are numerous software options available for creating 3D maps, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular choices include:
- ArcGIS Pro: A powerful GIS software suite that includes advanced 3D mapping capabilities.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that offers a range of 3D mapping tools.
- SketchUp: A user-friendly 3D modeling software that is popular for creating architectural and urban models.
- Blender: A free and open-source 3D modeling and animation software that can be used for creating 3D maps.
- 3ds Max: A professional 3D modeling and animation software that offers advanced features for creating complex 3D maps.
Tips for Creating Effective 3D Maps
- Define the purpose and audience: Before embarking on 3D map creation, clearly define the purpose of the map and the intended audience. This will guide the selection of data, the level of detail, and the overall design.
- Choose the right software: Select software that meets the specific needs of the project. Consider factors such as ease of use, feature set, and compatibility with existing data sources.
- Use high-quality data: The accuracy and quality of the data used to create 3D maps are crucial. Ensure that data is reliable, up-to-date, and relevant to the project objectives.
- Focus on clarity and simplicity: Avoid overwhelming the user with too much information. Prioritize clarity and simplicity, ensuring that the map effectively conveys the intended message.
- Use color and texture effectively: Color and texture can enhance the visual appeal and readability of 3D maps. Use these elements strategically to highlight key features and differentiate between different data layers.
- Incorporate interactive elements: Interactive features, such as zoom, pan, and rotation, can enhance user engagement and provide a more immersive experience.
- Test and refine: Thoroughly test the 3D map before sharing it with others. Ensure that it functions correctly, is visually appealing, and effectively communicates the desired information.
Conclusion
3D map creation is a powerful tool for visualizing, analyzing, and communicating spatial information. Its ability to provide a more immersive and interactive understanding of geographic data has revolutionized various fields, from urban planning and environmental monitoring to resource exploration and education. As technology continues to evolve, 3D map creation software is expected to become even more sophisticated and accessible, further expanding its applications and impact on our understanding of the world around us.






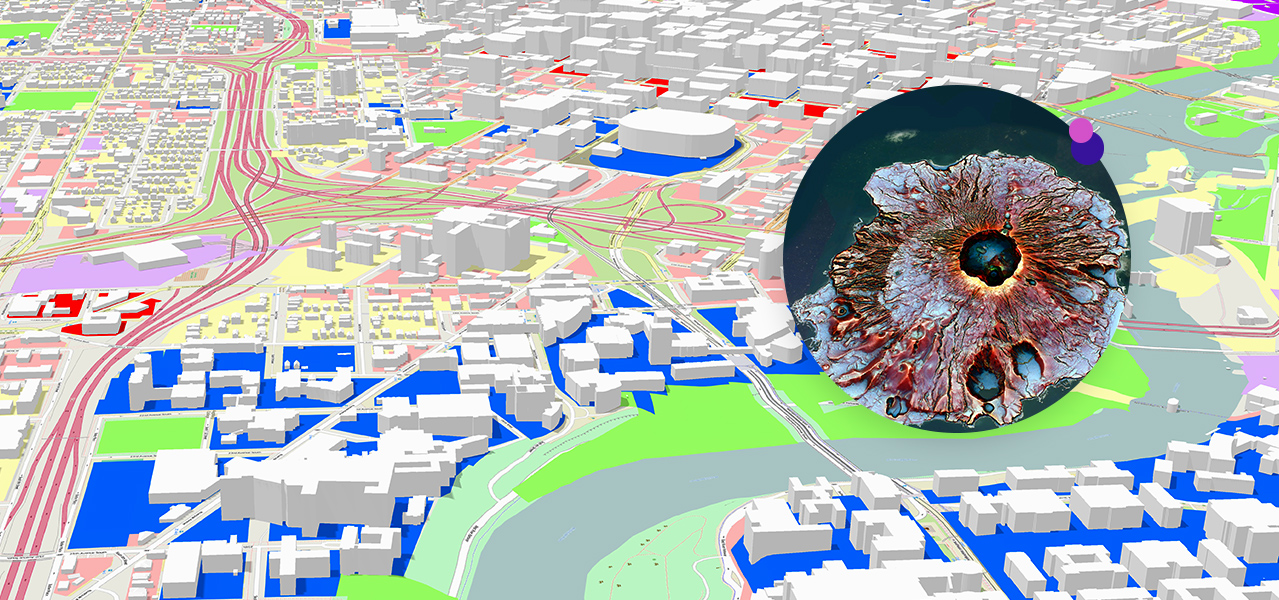
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visualization: A Deep Dive into 3D Map Creation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!