Unveiling Montana’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Montana’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Montana’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Montana’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps
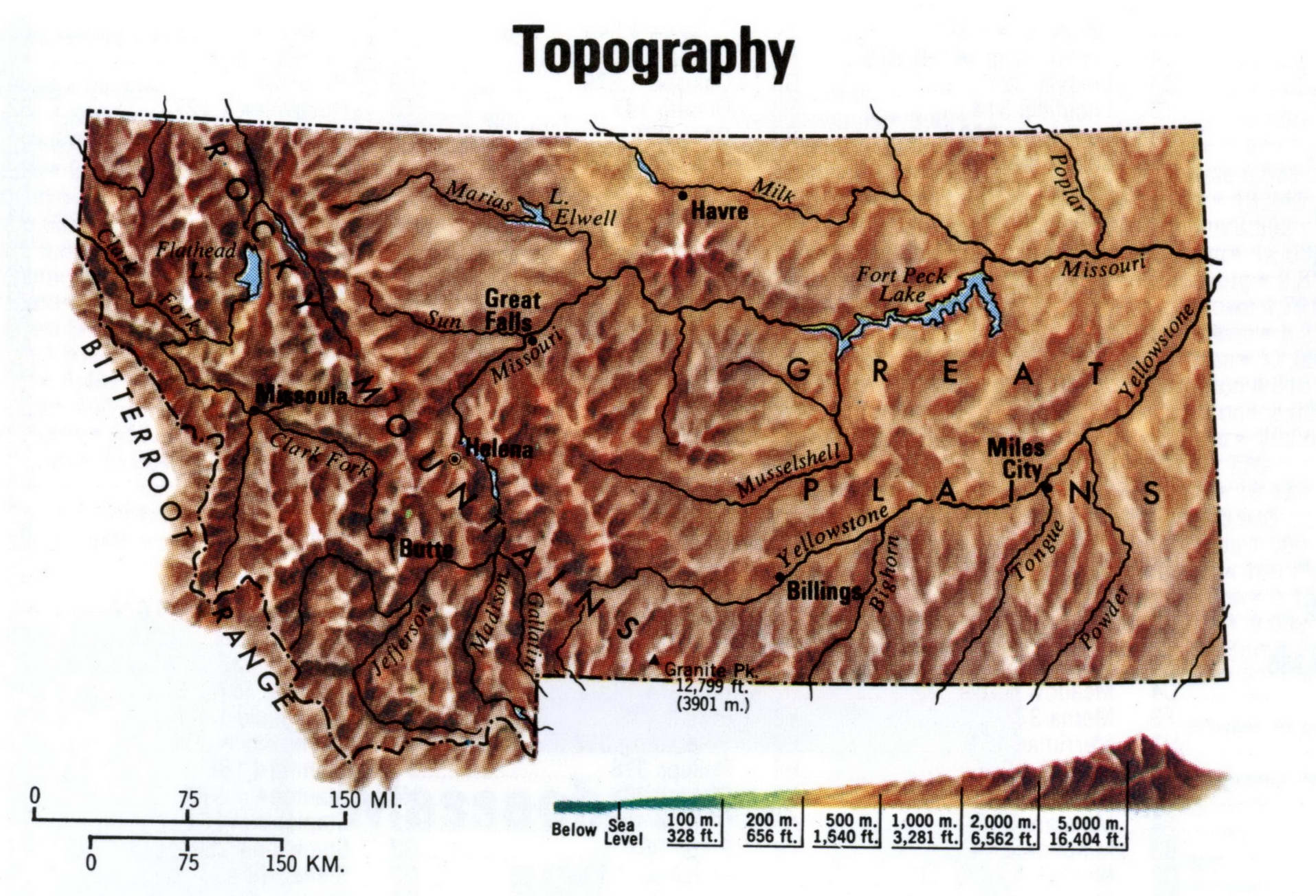
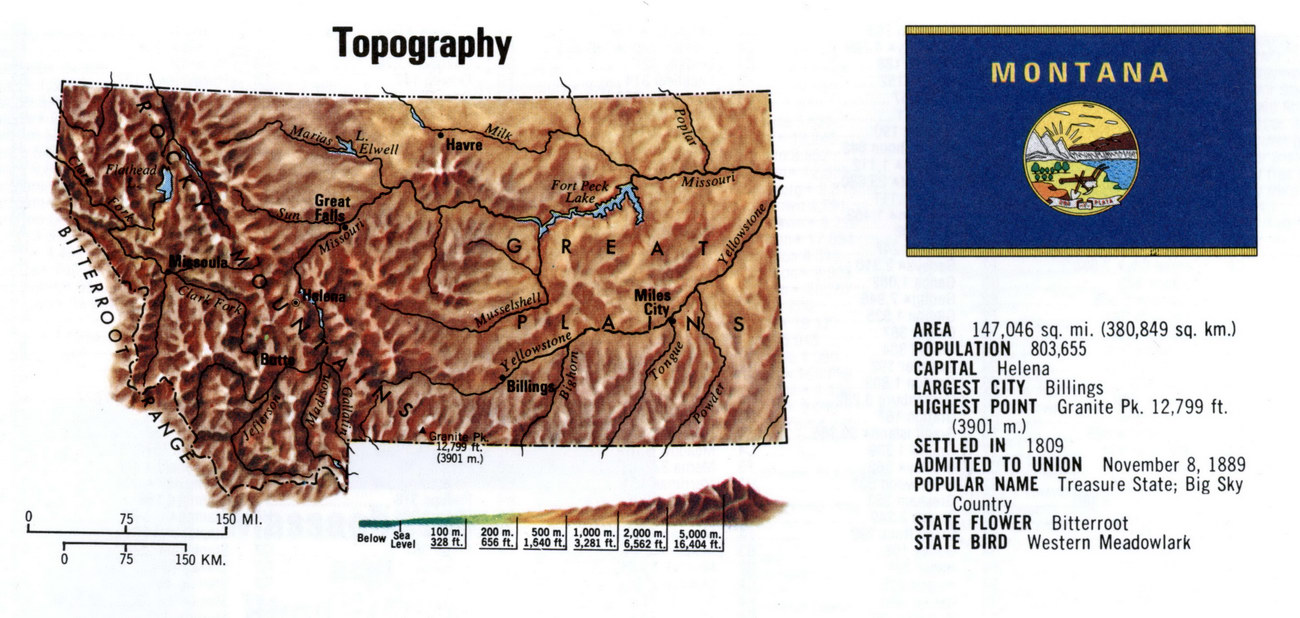
Montana, the "Treasure State," boasts a landscape of breathtaking beauty and unparalleled diversity. From the towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the rolling plains of the eastern region, the state’s topography is a testament to its geological history and a driving force behind its unique ecosystem and cultural identity. Understanding this intricate tapestry of mountains, valleys, rivers, and plains requires a tool that goes beyond basic maps: topographic maps.
The Essence of Topographic Maps:
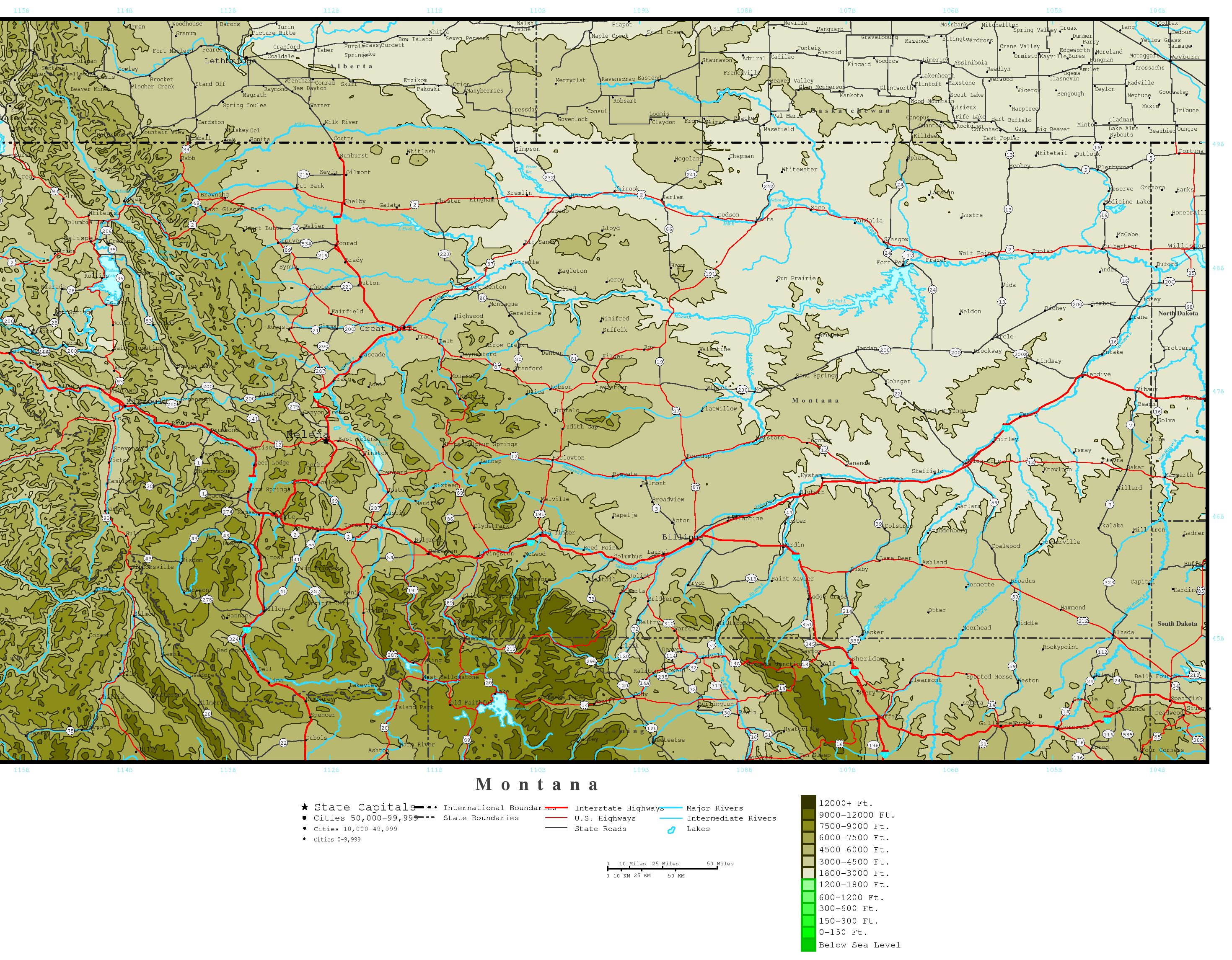
Topographic maps are specialized cartographic representations that depict the Earth’s surface in three dimensions. They employ contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to create a visual representation of terrain features. These lines, like the rings of a tree, reveal the rise and fall of the land, showcasing hills, valleys, ridges, and depressions. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the terrain; the further apart they are, the gentler the slope.
Montana’s Topographic Landscape:
Montana’s topographic map is a captivating story of geological forces shaping the land over millennia. The most prominent feature is the Rocky Mountains, a formidable spine running through the western portion of the state. These mountains, formed by tectonic plate collisions, rise dramatically, reaching heights exceeding 12,000 feet in Glacier National Park. The rugged peaks, deep canyons, and alpine meadows present a challenging yet rewarding landscape for outdoor enthusiasts.
East of the Rockies lies the Great Plains, a vast expanse of relatively flat terrain that stretches eastward towards the Missouri River. This region, characterized by rolling hills and grasslands, was once a vast sea before tectonic uplift and erosion sculpted its present form. The plains provide a stark contrast to the rugged mountains, offering a different perspective on Montana’s diverse topography.
Beyond Elevation: The Importance of Topographic Maps:
Topographic maps are essential tools for a myriad of purposes in Montana, offering invaluable insights into the state’s landscape and its impact on various aspects of life.
-
Outdoor Recreation: For hikers, backpackers, skiers, and climbers, topographic maps are indispensable for planning routes, assessing terrain difficulty, and ensuring safety. They reveal potential hazards like steep slopes, cliffs, and water crossings, allowing for informed decision-making.
-
Resource Management: Understanding the terrain is crucial for managing natural resources, including water, timber, and wildlife. Topographic maps help identify potential areas for water storage, delineate watersheds, and analyze the impact of land use on wildlife habitats.
-
Infrastructure Development: From road construction to pipeline routing, topographic maps provide critical data for infrastructure projects. They help identify suitable locations for construction, assess potential environmental impacts, and optimize project design.
-
Emergency Response: In the event of natural disasters like floods, wildfires, or earthquakes, topographic maps aid in disaster response efforts. They provide crucial information about terrain features, access routes, and potential evacuation zones.
-
Scientific Research: Topographic maps are vital for various scientific disciplines, including geology, ecology, and climatology. They enable researchers to study landforms, analyze geological processes, and model the effects of climate change on the environment.
Navigating Montana’s Terrain: Understanding the Map:
To effectively utilize topographic maps, it is essential to understand the key elements and symbols used in their construction.
-
Contour Lines: The most prominent feature of topographic maps, contour lines connect points of equal elevation. They provide a visual representation of the terrain’s shape, with closely spaced lines indicating steep slopes and widely spaced lines representing gentler slopes.
-
Elevation: The elevation of specific points on the map is typically indicated by numbers, allowing users to determine the height of features like peaks, valleys, and water bodies.
-
Symbols: Various symbols represent different features on the map, including roads, trails, buildings, water bodies, and vegetation. A legend accompanying the map provides a key to these symbols, enabling users to interpret the information accurately.
-
Scale: The scale of the map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Understanding the scale is crucial for accurately measuring distances and estimating travel times.
FAQs about Topographic Maps in Montana:
Q: Where can I find topographic maps of Montana?
A: Topographic maps of Montana can be obtained from various sources, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS provides a vast collection of topographic maps, both in print and digital formats, covering the entire state.
- Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation (DNRC): The DNRC offers topographic maps specific to certain regions and parks within Montana.
- Outdoor Recreation Retailers: Many outdoor recreation retailers carry topographic maps of Montana, providing a convenient option for purchasing them.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Websites like Google Maps and ArcGIS Online offer interactive topographic maps that can be accessed online.
Q: What are the different types of topographic maps available for Montana?
A: Topographic maps of Montana come in various formats and scales, catering to different needs and purposes.
- 7.5-minute Quadrangle Maps: These are the most common topographic maps, covering an area of approximately 7.5 minutes of longitude and latitude. They offer a detailed representation of the terrain and are suitable for hiking, backpacking, and other outdoor activities.
- 15-minute Quadrangle Maps: These maps cover a larger area and provide a less detailed representation of the terrain. They are suitable for regional planning and resource management.
- Statewide Topographic Maps: These maps provide a general overview of the state’s topography and are useful for understanding the overall landform patterns.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These are digital representations of elevation data that can be used to create topographic maps and other visualizations.
Q: How can I use topographic maps for navigation?
A: Topographic maps can be used for navigation by following these steps:
- Orient the map: Align the map with your current location using a compass or GPS device.
- Identify your starting point: Locate your current position on the map.
- Plan your route: Trace your desired route on the map, considering terrain features, elevation changes, and potential hazards.
- Use landmarks: Identify prominent landmarks on the map and use them as reference points during navigation.
- Check your position: Periodically check your position using a compass, GPS, or other navigation tools to ensure you are staying on course.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps in Montana:
- Choose the appropriate map scale: Select a map scale that provides sufficient detail for your intended activity.
- Study the map before venturing out: Familiarize yourself with the terrain, elevation changes, and potential hazards before embarking on your trip.
- Carry a compass and GPS device: These tools are essential for navigation, especially in areas with limited visibility.
- Mark your route on the map: Use a pencil or pen to trace your intended route, making it easier to follow.
- Be aware of weather conditions: Changing weather can significantly impact terrain conditions, so check forecasts and be prepared for potential hazards.
- Practice map reading skills: Regularly practice using topographic maps to improve your navigation abilities.
Conclusion:
Topographic maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding, navigating, and appreciating Montana’s diverse and captivating landscape. They provide a detailed representation of the terrain, offering insights into elevation changes, landform features, and potential hazards. Whether for outdoor recreation, resource management, infrastructure development, emergency response, or scientific research, topographic maps play a crucial role in understanding and interacting with Montana’s unique environment. By mastering the art of reading and interpreting these maps, individuals can unlock the secrets of Montana’s terrain and experience its natural beauty to the fullest.
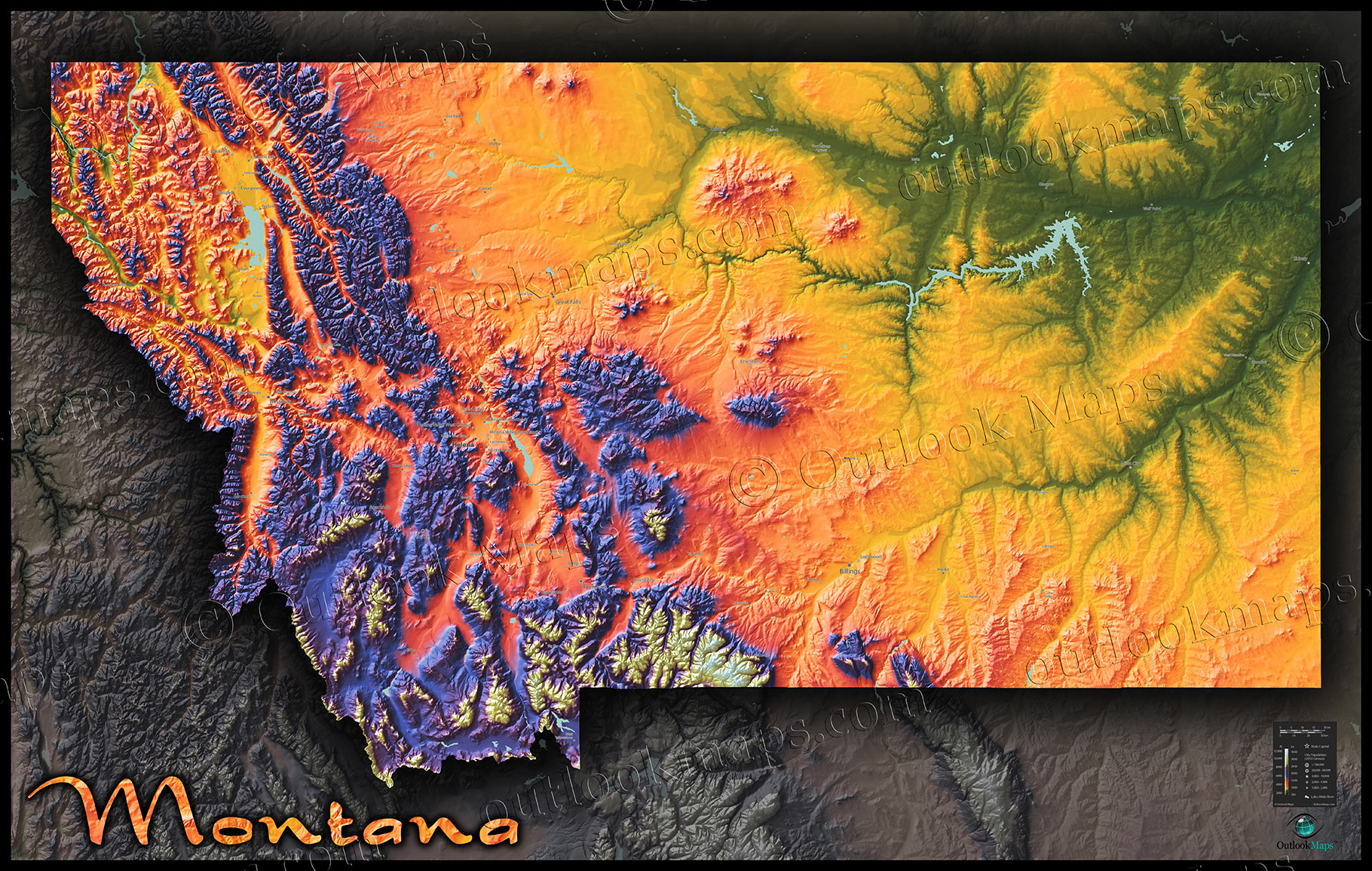
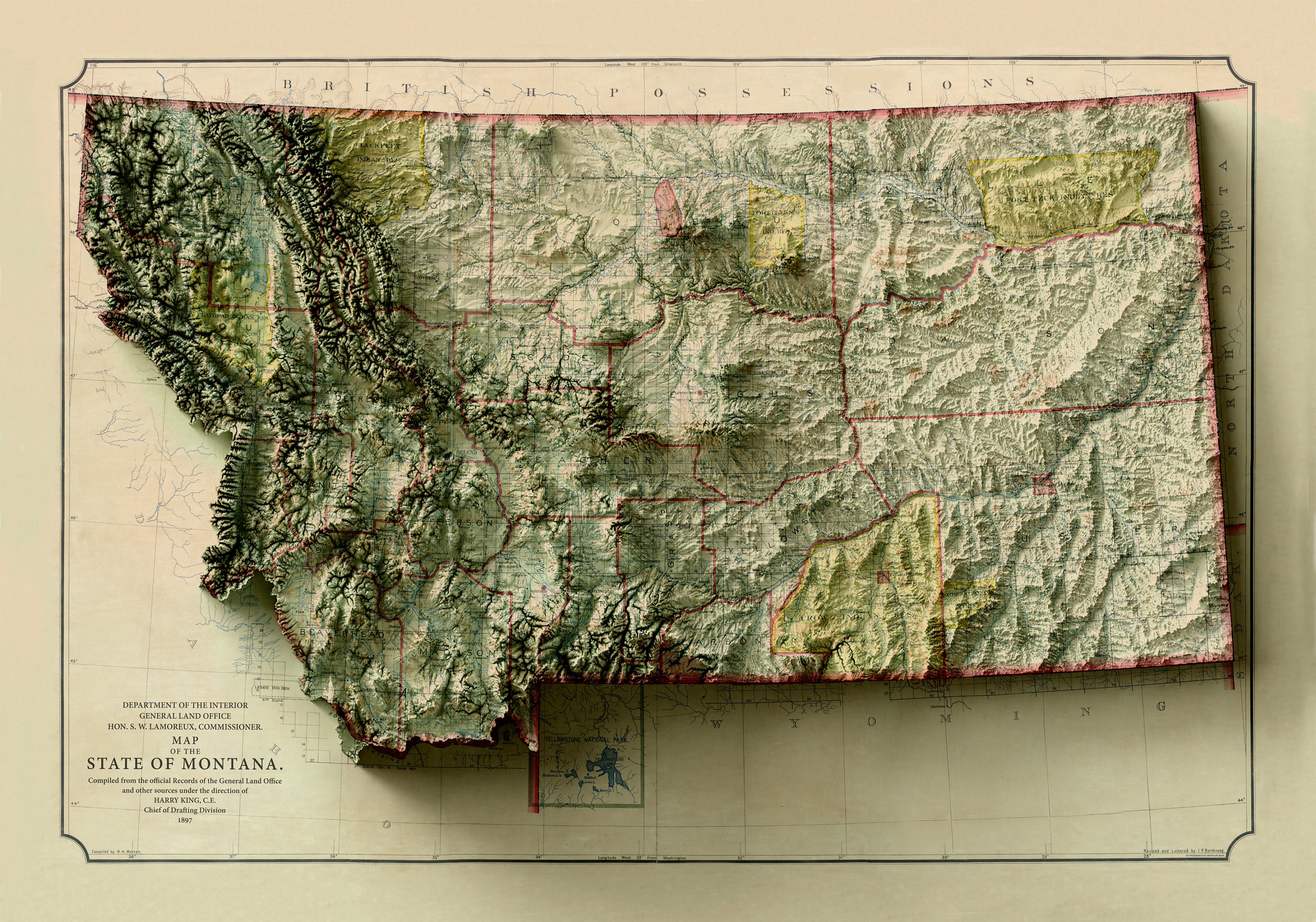

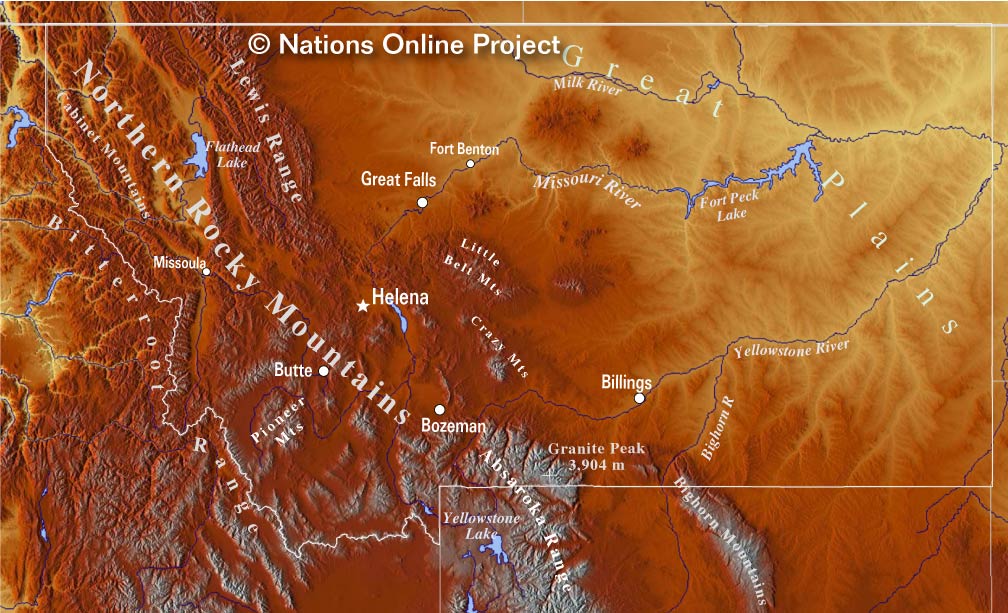

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Montana’s Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!